Symptom
Overcoming Intense Joint Pain
A recent poll completed by the University of Michigan has found that 70% of adults between the ages of 50 and 80 have experienced symptoms of joint pain or arthritis, with women being 10% more likely to report discomfort than men.
Gout, for example, is one of the most common types of inflammatory arthritis that can cause sudden, intense joint pain. Interestingly, it is a condition more common in men than in women and will often come in flares, lasting two to three weeks at a time. However, some other forms of joint discomfort and arthritis can be persistently painful problems.
Regardless of the cause, intense joint pain can begin interfering with your daily activities and overall well-being if left untreated. You see, individuals suffering from joint discomfort can experience many uncomfortable symptoms, including aches and pains, stiffness, reduced range of motion, grating sensations within the joint, and joint swelling.
Additionally, longstanding joint discomforts are often a challenging symptom to manage, having a long-standing influence on a person’s overall quality of life. This can include reduced normal mobility, which disrupts basic daily tasks, social isolation, and an increased risk of depression.
The University of Michigan’s 2022 National Poll on Healthy Aging also found that 66% of people reported taking over-the-counter pain relievers for their joint pain, which, if taken for an extended period, may begin to impact a person’s general health, particularly their stomach and liver.
Properly addressing all forms of joint pain is an essential aspect of supporting normal and comfortable movements, preventing pain, and maintaining quality of life as we age.
This article will cover the fundamental concepts of joint pain, including the causes and potential medical conditions typically associated with it. We’ll also share vital insights into how doctors approach a joint pain diagnosis, as well as the most typically prescribed treatment options.
We’re excited to present the Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management solutions, offering a promising approach for individuals to alleviate their joint discomfort. Explore how Neurofunctional Pain Management can effectively address pain and inflammation associated with various chronic health conditions, all without relying on harsh drugs or surgical procedures.
Now, let’s get right in and discover more about joint pain and the range of presenting features it can have.
What Is Joint Pain?
Arthralgia is the medical term for joint pain in any joint of the body. Ranging from slight irritation to severe discomfort, the extent of associated symptoms for joint pain will largely depend on the underlying cause and can vary greatly between individuals.
Joint pain can affect a single joint (arthralgia) or multiple joints simultaneously, a condition called polyarthralgia or polyarticular pain. Much like the symptoms, the number of joints affected will depend on the cause and severity of the joint pain and whether it’s linked to a specific illness or injury.
Arthralgia can stem from a range of factors such as injury, overexertion, strain, or poor posture during certain movements that were performed before the pain appeared. For example, if a person experiences discomfort in their knee after a strenuous workout or doing chores, it is likely arthralgia specific to that joint.
Polyarticular pain, on the other hand, affects several joints and is commonly seen in medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout. In scenarios such as these, pain tends to be more widespread and generally leads to a more impactful effect on a person’s ability to perform daily activities and on their overall quality of life.
Gaining this understanding of being able to differentiate between joint pain that is arthralgia or polyarticular helps guide an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. It provides a deeper insight into your condition, helping you and your doctor rule out underlying causes and tailor their diagnostic tests and interventions accordingly.
For instance, if you tell your doctor that you are experiencing pain in many of your joints, being polyarticular, it is more likely that a systemic condition such as rheumatoid arthritis may be considered, necessitating a different approach compared to localized joint pain that may be more indicative of a joint sprain or tissue damage.
Perhaps you’ve recently suffered from a joint injury where the pain is lingering or getting worse. Or, if you’re not sure what’s causing your pain and are starting to experience it through multiple joints, it’s normal to be curious as to what the underlying causes may be. In the next section, we’ll explore the risk factors of intense joint pain.
Risk Factors For Joint Pain
Joint pain, both arthralgia and polyarticular, is caused by a wide range of underlying variables. We’ve included a list of some of the most prevalent risk factors below:
- Injury or trauma: Sustaining injury and trauma to a joint, such as fractures or dislocations, can result in acute joint pain. It’s essential to seek proper medical attention and rehabilitation strategies for a successful recovery to prevent further damage that will cause more problems later on.
- Strain: Overuse or repetitive motion can result in strain on the joint and its surrounding structures, causing acute pain. This is common in occupations or activities that involve repetitive movements, such as bricklaying or high-impact sports.
- Poor posture: An incorrect posture, especially when sustained for long periods, is highly likely to contribute to joint pain, e.g. neck pain from desk work. Ensuring you have a good ergonomic setup and a supportive posture is essential for joint health.
- Lack of exercise: Engaging in regular exercise helps to keep joints flexible as well as strengthen their surrounding ligaments and muscles. Lack of exercise can lead to joint weakness and imbalances, contributing to pain.
- Inactivity and immobility: Leading a sedentary lifestyle or experiencing prolonged periods of inactivity can lead to joint stiffness and discomfort. Even just a short walk or some chair exercises done daily could make a difference and improve your joint health.
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight puts additional stress on joints, particularly those in the knees, hips, and lower back.
Understanding the underlying causes of joint pain can help you proactively improve your joint health and develop effective pain management strategies that target the underlying cause. In the next section, we’ll discuss the medical conditions that can lead to painful joints in more detail.
Medical Conditions That Can Cause Intense Joint Pain
Intensely painful joints are well known to be triggered by a number of medical conditions. For most people, chronic arthritis is the first medical condition that comes to mind.
You might find it interesting to learn that arthritis is the medical term to describe joint swelling or inflammation, which can actually encompass more than 100 joint and joint-related conditions.
While osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common forms of arthritis, this term can also be used for less suspecting conditions such as gout, fibromyalgia, and ankylosing spondylitis.
It’s important to remember that if your pain is becoming an ongoing problem, there may be an underlying explanation. Let’s explore some of the more common ones below:
Rheumatoid Arthritis
As an auto-immune form of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by the immune system getting confused and attacking your joints instead of protecting them. The damage caused by the immune system leads to inflammation and swelling in the lining of the joints, causing pain and reduced mobility. It can sometimes even cause visible joint disfigurement.
Septic Arthritis
Septic arthritis is a condition where swelling and inflammation of the joint occur as a result of infection. This particular form of arthritis is not a pleasant experience, as infection within the tight joint space can lead to intense pain and discomfort. If not treated quickly, this condition can lead to lasting joint damage, or the infection may spread into the bone and generate major complications. If you have a reason to believe your joint may be infected, it is highly recommended you seek prompt medical attention.
Bursitis
Bursitis is a different form of joint pain that commonly affects larger joints such as the shoulders, hips, knees, and elbows. The bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion these large joints, allowing them to move smoothly. When the bursae become inflamed and irritated, this is called bursitis. It can occur due to overuse, strain, or degeneration (wear and tear) and leads to significant pain and stiffness, requiring rest and rehabilitation.
Tendonitis
Our tendons are close neighbors to our joints, connecting muscles to bone. Every time you contract your muscles, it’s the tendons that harness that power for limb movement. Tendonitis occurs when tendons become inflamed from overuse or injury, which can lead to pain and tenderness around the affected area, including the joints.
Understanding more about these conditions helps you have a better idea of what might be causing your intense joint pain. If you already have a diagnosis and are looking for relief from ongoing discomfort, keep reading to learn how we can help.
Conditions Causing Joint Pain That We Treat
We specialize in Neurofunctional Pain Management, providing non-pharmaceutical, non-chiropractic, and non-surgical solutions to help manage joint pain from various conditions, such as:
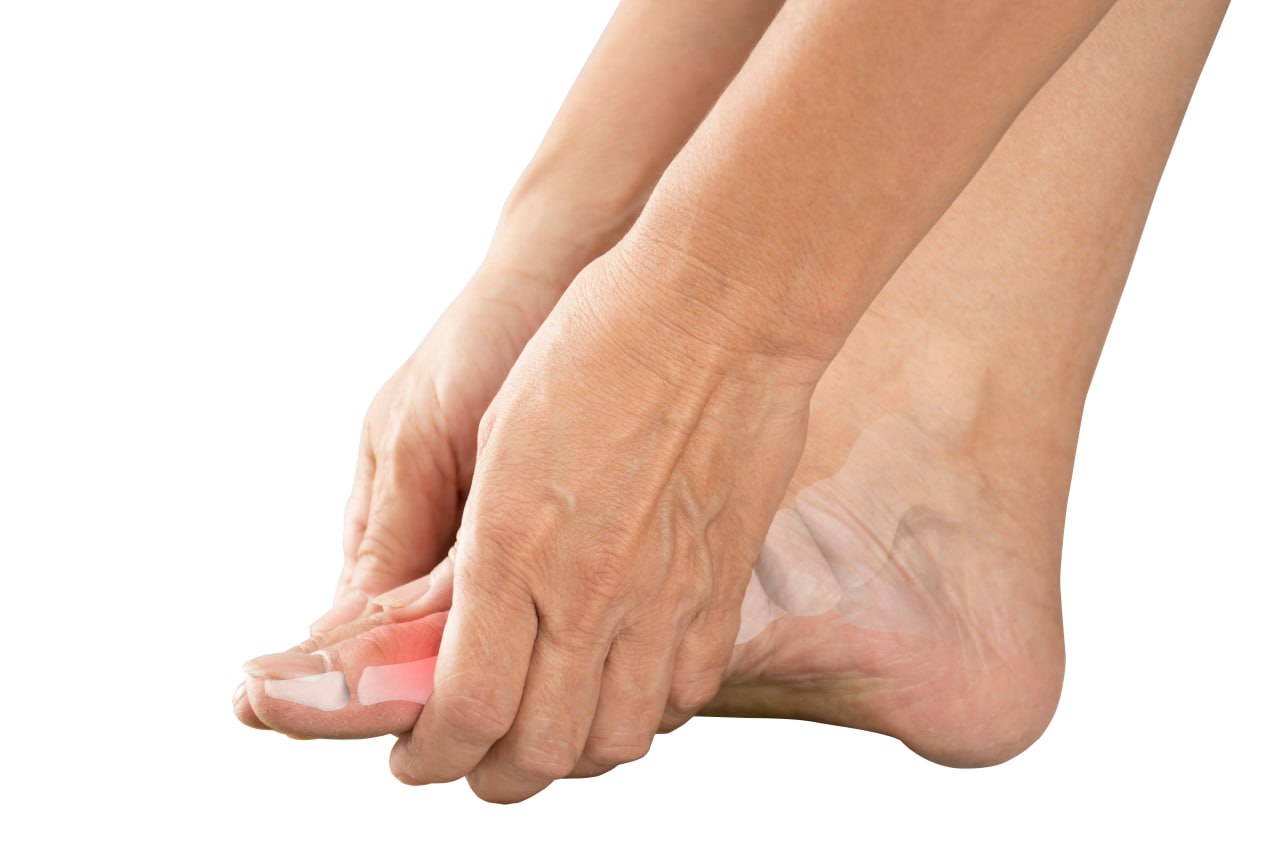
Gout Pain Treatment
Gout is a painful condition that can cause severe joint inflammation and swelling. It can lead to chronic pain and mobility issues that can have an enormous impact on your quality of life. Fortunately, the Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management protocol...
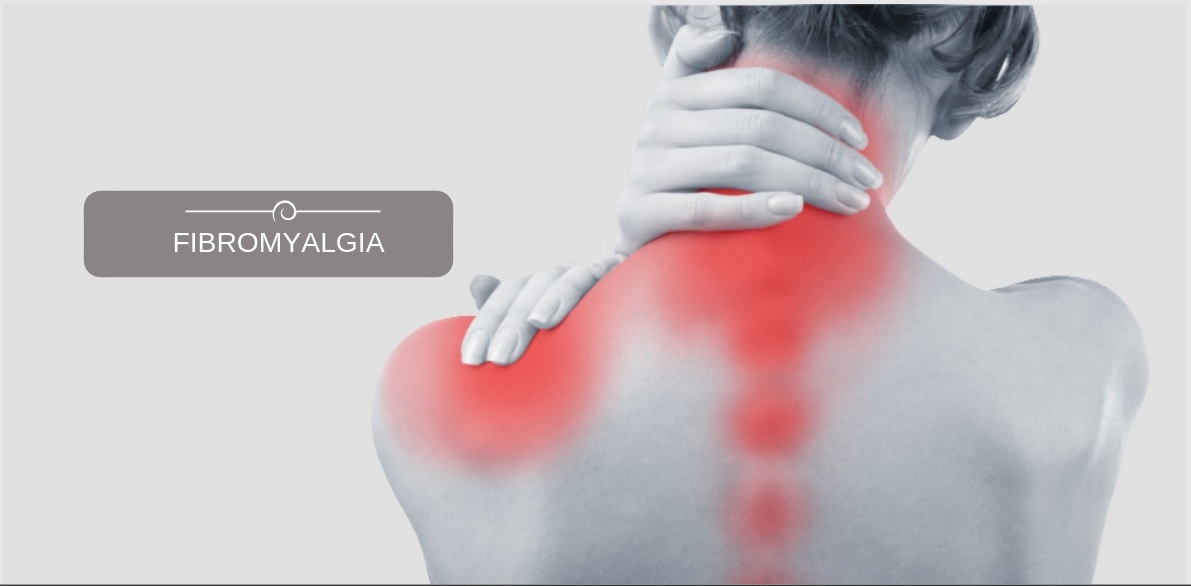
Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder that causes several symptoms, including widespread pain, fatigue, and cognitive impairment. Our non-surgical and drug-free treatments can help reduce the chronic pain associated with fibromyalgia. Additionally, our holistic...
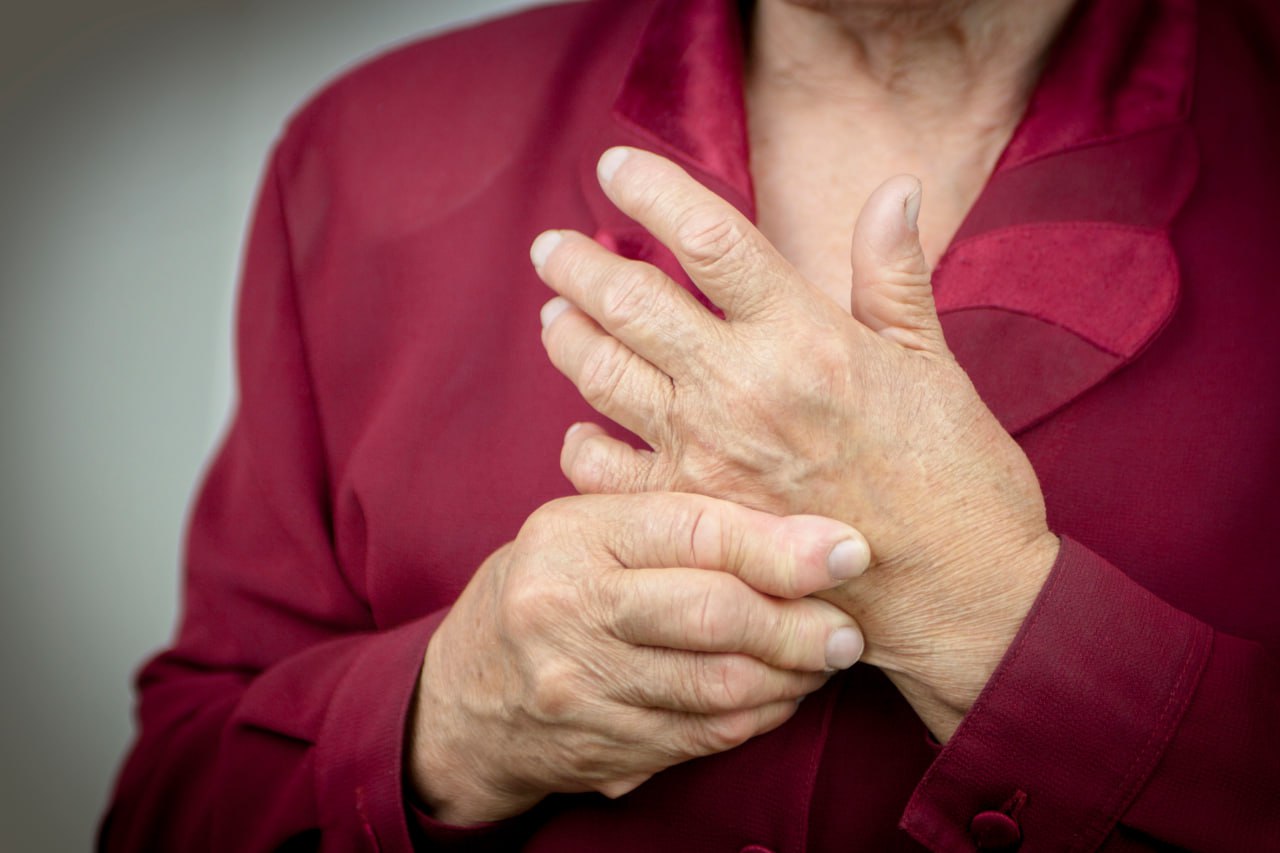
Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment
Rheumatoid arthritis can be a debilitating and painful condition that causes swelling, joint damage, and immobility. We offer a non-invasive, non-chiropractic solution to alleviate the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Our treatments are designed to...

Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment
Osteoarthritis is often linked to joint pain. But the impact that this condition has on your life is of much greater magnitude. If you have osteoarthritis, the chances are that you experience a pain so intense that it prevents you from climbing stairs,...
Joint Pain Diagnosis: Seeking Medical Attention
If you are unsure of what is causing your joint pain, or if you notice any of the following symptoms, it is advisable to make an appointment to speak to your doctor:
- Severe joint pain that interferes with your daily activities
- Intense joint pain that comes on suddenly
- Joint pain coupled with swelling, redness, and warmth around the joint
- Joint pain with a visible deformity
- Reduced range of motion or inability to use the joint
Your doctor will likely conduct various tests to identify the cause of your joint pain. In the list below, we have set out some of the typical methods you can expect your doctor to use.
- Medical history and symptom discussion: Doctors often begin by asking you about your medical history and current symptoms, trying to understand your condition better.
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination should be conducted to assess for any joint limitations, reduction of mobility, signs of inflammation, or other abnormalities that could be contributing to your pain. You can expect the doctor to assess joints that aren’t painful, for comparison purposes.
- Imaging tests: Various imaging tests may be ordered, such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans. These tests help provide a detailed view of the joint and its neighboring structures, revealing any abnormalities in the bones, muscles, and tendons.
- Blood tests: Blood tests are great indicators of general health. They are mostly used in cases of joint pain to identify markers of inflammation or specific immune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Joint fluid analysis: In some cases, a small sample of joint fluid is withdrawn from the affected joint to test for infections or the presence of gout crystals.
Completing a comprehensive evaluation of your painful joints is important to identify the root cause and ensure you receive a personalized and effective management plan. We hope these insights provide you with an understanding of what to expect when seeking medical help for your joint pain.
Let’s now look into some of the conventional therapies commonly recommended for various degrees of painful joints.
Common Treatments For Intensely Painful Joints
In the journey of managing joint pain, there are a number of conventional treatments that can help provide varying degrees of pain relief, depending on the underlying cause. The primary goal is to alleviate pain, target the root cause, enhance joint mobility, and of course, find a sense of normalcy again.
The management process will usually begin with rest and rehabilitation and then jump into pharmaceutical and, if necessary, surgical options. Let’s explore the conventional process of managing joint pain in more detail below:
Heat And Cold Therapy
Joint pain can be eased with the simple yet effective application of heat or cold. A straightforward technique is easily applicable at home. Heat pads, a warm bath, and cold packs (or the trusty frozen peas) can be very effective at providing soothing relief. You may want to alternate between hot and cold treatments to see what is most beneficial for you.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a tailored approach to improving muscle strength and flexibility. It may help reduce painful joints as it promotes improved stabilization and smoother movements. It’s important to see a licensed physical therapist to create a customized exercise program that addresses your specific needs, promotes recovery, and prevents further injury.
Medications
To manage your pain and improve joint function, a doctor may suggest a variety of medications based on the underlying cause. These can range from over-the-counter options like acetaminophen along with anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or celecoxib.
And for specific conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs may also be incorporated into the treatment plan. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable medication based on your individual needs and the nature of your joint pain.
Injections
For chronically stubborn pain, corticosteroid injections can be used as a more direct approach. They are often recommended for injuries that have caused significant swelling and conditions such as bursitis or various types of arthritis. These injections aim to reduce inflammation, providing more localized and immediate relief.
Surgery
In severe cases, and where all other conservative and alternative measures have been unsuccessful, surgical interventions may become an option. This is because surgical techniques are more invasive, which makes them susceptible to complications.
When there are severe joint injuries or structural concerns, procedures like an arthroscopy or joint replacement can be considered to provide long-term relief.
Arthroscopy
An arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that assists in diagnosing and treating complex joint conditions. Otherwise known as “key-hole surgery,” it involves the surgeon making a small incision to access the affected joint. A small camera helps the surgeon assess the joint, and small tools may be used to help remove debris and repair damaged structures.
Joint Replacement
A joint replacement is a largely invasive procedure that involves the partial or full removal of a joint and replacing it with a prosthetic. A joint replacement will typically involve a longer recovery and rehabilitation period.
It’s important to note that each of these treatment options for joint conditions will have its own unique effectiveness and potential for side effects. Additionally, in best practice, a strong emphasis should be placed on using conservative treatments to promote joint health and reduce discomfort before considering invasive therapies.
To make the best choices for your health management, talk to your medical professionals to become well-informed about all the treatment options available to you.
For many individuals dealing with chronic joint pain, the conventional management process might not provide the long-lasting results they’ve been looking for. Let’s now shift our focus to discuss an alternative pain management solution offered by Neuragenex.
Neurofunctional Pain Management To Treat Joint Pain
The team members are experts in Neurofunctional Pain Management (NFPM), an innovative approach that goes beyond conventional processes to help control painful symptoms.
NFPM combines three specially designed therapies that work together to address the pain and inflammation associated with various conditions and injuries contributing to joint discomfort.
The most important feature of the Neuragenex NFPM approach, in our opinion, is that it is proudly non-pharmaceutical, non-chiropractic, and non-surgical, including the following therapies:
Electroanalgesia
Electroanalgesia is a pain management technique that uses high-pulse electrical current to ease pain, boost blood circulation, improve mobility, and induce...
IV Therapy
IV nutritional therapy, or intravenous therapy, involves administering vital nutrients directly to the bloodstream through an IV. This type of treatment bypasses the digestive system, allowing for maximum absorption and utilization of nutrients by the...
Lifestyle Counseling
Lifestyle counseling is an approach to managing chronic pain that involves identifying, assessing, and modifying lifestyle factors contributing to an individual's pain. For example, lifestyle factors such as nutrition, physical activity, stress, sleep quality...
Maintaining Optimal Joint Health: Tips and Tricks
In addition to medical interventions, we strongly advocate that preventing injuries and minimizing wear and tear are significantly beneficial for maintaining healthy joints as you age.
We have put together this list of practical steps you may wish to add to your wellness routine for the health of your joints:
- Stretch and exercise regularly: Physical activity promotes joint flexibility and strength. Low-impact exercises such as yoga, swimming, and cycling are all great for joint health.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Managing a healthy weight helps to reduce the stress and impact throughout your weight-bearing joints.
- Incorporate joint-friendly foods: Foods rich in calcium, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants can all be greatly beneficial for bone and joint health.
- Protect your joints during physical activities: When doing exercise, be sure you are using proper techniques and wearing protective gear such as ankle or wrist straps if necessary.
- Get quality sleep: Our sleep quality has a large impact on our overall health, including joint health. Ensuring you get 7-8 hours of quality sleep can greatly benefit joint recovery.
We trust that these pointers will help you improve the health of your joints and reduce the risk of joint pain negatively impacting your quality of life.
Take Steps To Safeguard Your Joints
Joint pain has the potential to greatly impact the normalcy and quality of life of many individuals. However, having a clear understanding of the underlying causes and symptoms can empower you to seek appropriate care to manage and prevent intense joint pain.
Many self-help measures and conventional treatments can provide temporary relief. Yet, many people seek alternative treatment approaches to avoid extended medication use and invasive procedures while still directly addressing the root causes of pain and inflammation.
We are dedicated to providing innovative solutions to empower individuals suffering from joint pain. Whether it’s gout pain, arthritis, fibromyalgia, or rheumatoid arthritis, the Neurofunctional Pain Management protocols we provide offer a personalized approach and hope for individuals to find lasting relief.
Remember, maintaining your joint health is an important part of your overall well-being as you get older. Our goal is to provide you with the tools and therapies that promote a life free from the burden of joint pain and magnify your quality of life.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights and practical tips for managing intense joint pain effectively. If you have any questions or are seeking non-invasive approaches to manage your joint pain, contact us today.
Could the underlying cause of your excruciating joint pain be gout? Prioritize your joint health. Embrace a life free from pain and discomfort starting today.


You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/
You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/
Insurance Form
-
Neurofunctional Pain Management Overview
-
Symptoms
- A Lump on the Tendon
- Pain With Intercourse
- Bicep Muscle Spasm
- Bicep Tendon Pain
- Calf Tendon Pain
- Throbbing Headache Only in Affected Areas
- Sudden Weight Gain or Loss
- Increase in Bowel Movements
- Chronic Foot Pain
- Cognitive Impairment
- Collateral Ligament Pain
- Crepitus
- Dull Headache
- Difficulty Walking
- Digestive Issues
- Sensation of Numbness
- Vein Pain
- Urge to move legs
- Foot Ligament Pain
- Front Thigh Muscle Pain
- Infertility
- Intense Pain in Joints
- Irritability or Fatigue
- Jaw Locking
- Joint Swelling
- Joint Stiffness & Swelling
- Loss of Movement in Lower Body
- Lower Back Swelling or Redness
- Lower Leg Muscle Loss
- Muscle Cramps in Legs at Night
- Muscle Spasms in back of Thigh
- Muscle Spasms in Neck
- Muscle Spasms in Rib Cage
- Muscle Spasms in Arm
- Muscle Spasms in Stomach
- Muscle Spasms near Elbow
- Muscle Spasms in Pelvic Floor
- Muscle Spasms
- Muscle Spasms in the Armpit
- Muscle Spasms in the Chest
- Muscle Spasms in the Hands
- Muscle Weakness & Paralysis
- Nasal Congestion
- Neck Pain
- Numbness and Tingling in Fingers
- Pain & Discomfort in Arms or Legs
- Neuralgia
- Pain in Hand & Wrist
- Peroneus Brevis Tendon Pain
- Jaw Pain or Tenderness
- Painful Bowel Movements
- Lower Back & Leg Pain
- Painful Periods
- Patellar Tendon Pain
- Feeling of Pins & Needles
- Pupil Constriction
- Reduced Knee Mobility
- Sciatica Pain
- Sharp Pain under Heel or Foot Arch
- Shoulder Inflammation & Pain
- Limited Range of Motion
- Stomach is Swollen & Bloated
- Stomach Pain
- Tender Lymph Nodes
- Tendon Pain
- Tendon Pain Behind Knee
- Tingling Sensation in Hands & Feet
- Tinnitus
- Tiredness, Nausea, & Weakness
- Back Pain
- Muscle Tenderness
- Shoulder muscle spasms
- Tendon Swelling
- Tenderness & Pain When Touched
- Facial Flushing & Sweating
- Pain Between Shoulder Blades in Back
- Vein Pain Behind Knee
- Difficulty Focusing
- Excess Gas
- Tendon Pain in Neck
- Sensitivity to Light & Sound
- Hot or Warm Joint
- Sudden Hand Weakness
-
Conditions Treated
- Bone Fracture
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Chronic Knee Pain
- Cluster Headache
- Endometriosis
- Fibromyalgia
- Frozen Shoulder
- Gout
- Interstitial Cystitis
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Knee Pain
- Metabolic Dysfunction
- Migraines and Chronic Headaches
- Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Osteoporosis
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction
- Phantom Pain
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome
- Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Sciatica
- Sprained Ankle
- Substance Abuse Disorder
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- TMJ Dysfunction
- Tendonitis
- Tension Headaches
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
- Wrist Bone Fracture
-
Treatments
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Ankle Sprain
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Chronic Fatigue
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Chronic Migraines & Headaches
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Fibromyalgia
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Compartment Syndrome
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Endometriosis
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Frozen Shoulder
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Cluster Headaches
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Gout
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Interstitial Cystitis
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for IBS
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Long Covid
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Metabolic Dysfunction
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Neck & Back Pain
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Peripheral Neuropathy
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Osteoporosis
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasms
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Plantar Fasciitis
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Radial Tunnel Syndrome
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Restless Leg Syndrome
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Sciatica
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Joint Pain
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Tension Headaches
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Ulcerative Colitis
- Neurofunctional Pain Management for Urinary Incontinence
-
Articles by Category
- Anti Aging
- Allergy Testing
- Back Pain
- Biological Age
- Biphasic Electrical Stimulation
- Blood Test
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Chronic Knee Pain
- Cluster Headache
- Diabetes
- Disc Pain
- Electroanalgesia
- Endometriosis
- Fibromyalgia
- Frozen Shoulder
- Genetic Testing
- Gout
- Heavy Metal Testing
- Hip Pain
- Hormone Replacement Therapy
- IV Therapy
- Knee Pain
- Limb Pain
- Living With Chronic Pain
- Low Level Energy Laser (LLEL)
- Metabolic Dysfunction
- Microcurrent Electrical Therapy
- Migraine And Chronic Headaches
- Migraines
- Muscle Pain
- Muscle Spasms
- Muscle, Tendon, Ligament Pain
- Neuralgesia
- Neurofunctional Pain Management
- Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
- Non-Pharmaceutical Treatments
- Non-Surgical Treatment
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Sciatica
- Shoulder Pain
- Sleep Studies
- Sleep Therapy
- Sprained Ankle Pain
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder
- Tendonitis
- Tension Headache
-
Locations
-
Colorado
- Colorado Pain Management
- Baker
- Bear Valley
- Belcaro
- Brighton
- Capitol Hill
- Central Business District
- Cheesman Park
- Cherry Creek
- City Park
- City Park West
- Civic Center
- Congress Park
- Country Club
- East Colfax
- Goldsmith
- Hale
- Hampden
- Hampden South
- Harvey Park
- Harvey Park South
- Hilltop
- Lincoln Park
- Lowry
- Marston
- North Capitol Hill
- North Park Hill
- Park Hill
- Platt Park
- Ruby Hill
- Speer
- South Park Hill
- University
- University Hills
- University Park
- Washington Park
- Washington Park West
- Washington Virginia Vale
- Wellshire
- Windsor
- Broomfield
- Dacono
- Erie
- Firestone
- Fort Lupton
- Frederick
- Hudson
- Lafayette
- Lochbuie
- Louisville
- Northglenn
- Superior
- Thornton
- Westminster
- Fort Collins
- Greeley
- Johnstown
- Longmont
- Loveland
- Fountain
- Manitou Springs
- Monument
- Palmer Lake
- Peyton
- Security Widefield
- Arvada
- Commerce City
- Denver
- Federal Heights
- Henderson
-
Wisconsin
- Wisconsin Pain Management
- Appleton
- Beaver Dam
- Brookfield
- Brooklyn
- Burke
- Caledonia
- Chippewa Falls
- Cottage Grove
- Cross Plains
- Cudahy
- De Pere
- DeForest
- Doylestown
- Dunn
- Eau Claire
- Fall River
- Fitchburg
- Fond du Lac
- Franklin
- Germantown
- Green Bay
- Greenfield
- Hudson
- Janesville
- Kenosha
- La Crosse
- Lodi
- Madison
- Manitowoc
- Maple Bluff
- Marshfield
- Marshall
- McFarland
- Menasha
- Menomonee Falls
- Mequon
- Middleton
- Milwaukee
- Monona
- Mount Pleasant
- Muskego
- Neenah
- New Berlin
- Oak Creek
- Onalaska
- Oregon
- Oshkosh
- Platteville
- Pleasant Prairie
- Pleasant Springs
- Portage
- Poynette
- Prairie du Sac
- Racine
- Rio
- River Falls
- Rockdale
- Roxbury
- Sauk City
- Sheboygan
- South Milwaukee
- St. Francis
- Sun Prairie
- Watertown
- Waukesha
- West Allis
- West Bend
- Wisconsin Rapids
-
Georgia
- Georgia
-
Hiram
- Hiram Pain Management
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Bone Bruise Treatment in Hiram
- Broken Bone Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Hiram
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Hiram
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in Hiram
- Chronic Migraines and Headaches Treatment in Hiram
- Cluster Headaches Treatment in Hiram
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in Hiram
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Hiram
- Crohn’s Disease Treatment in Hiram
- Depression Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Hiram
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in Hiram
- Gout Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Immunotherapy Treatment in Hiram
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in Hiram
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in Hiram
- Joint Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Knee Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Long COVID Treatment in Hiram
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in Hiram
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in Hiram
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Neuragenex Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in Hiram
- Non-Steroidal Alternative to Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Hiram
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Pain from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Hiram
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasms Treatment in Hiram
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Hiram
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Restless Leg Syndrome Treatment in Hiram
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Hiram
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Hiram
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Tension Headaches Treatment in Hiram
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Trivisc Injections Treatment in Hiram
- Ulcerative Colitis Treatment in Hiram
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Hiram
- Urinary Incontinence Treatment in Hiram
- Vein Pain Treatment in Hiram
-
Lawrenceville
- Lawrenceville
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Bone Bruise Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Broken Bone Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Carpal Tunnel Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Cluster Headache Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Crohn’s Disease Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Depression Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Endometriosis Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Frozen Shoulder Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Gout Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Immunotherapy Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Joint Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Knee Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Long COVID Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Migraines and Headaches Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Neck and Back Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Neuragenex Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in Lawrenceville
- Non-Steroidal Alternative to Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Pain from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasms Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Restless Leg Syndrome Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Tension Headaches Treatment in Lawrenceville
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Trivisc Injections Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Ulcerative Colitis Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Urinary Incontinence Treatment in Lawrenceville
- Vein Pain Treatment in Lawrenceville
-
Marietta
- Marietta
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in Marietta
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Bone Bruise Treatment in Marietta
- Broken Bone Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Marietta
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Marietta
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in Marietta
- Chronic Migraines and Headaches Treatment in Marietta
- Cluster Headaches Treatment in Marietta
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in Marietta
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Marietta
- Crohn’s Disease Treatment in Marietta
- Depression Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Marietta
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in Marietta
- Gout Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Immunotherapy Treatment in Marietta
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in Marietta
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in Marietta
- Joint Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Knee Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Long COVID Treatment in Marietta
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in Marietta
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in Marietta
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Neuragenex Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in Marietta
- Non-Steroidal Alternative to Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Marietta
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Pain from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Marietta
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasms Treatment in Marietta
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Marietta
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Restless Leg Syndrome Treatment in Marietta
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Marietta
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Marietta
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Tension Headaches Treatment in Marietta
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Trivisc Injections Treatment in Marietta
- Ulcerative Colitis Treatment in Marietta
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Marietta
- Urinary Incontinence Treatment in Marietta
- Vein Pain Treatment in Marietta
-
Powder Springs
- Powder Springs
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in Powder Springs
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Bone Bruise Treatment in Powder Springs
- Broken Bone Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Powder Springs
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Powder Springs
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in Powder Springs
- Chronic Migraines and Headaches Treatment in Powder Springs
- Cluster Headaches Treatment in Powder Springs
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in Powder Springs
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Powder Springs
- Crohn’s Disease Treatment in Powder Springs
- Depression Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Powder Springs
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in Powder Springs
- Gout Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Immunotherapy Treatment in Powder Springs
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in Powder Springs
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in Powder Springs
- Joint Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Knee Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Long COVID Treatment in Powder Springs
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in Powder Springs
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in Powder Springs
- Neuragenex Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in Powder Springs
- Non-Steroidal Alternative to Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Powder Springs
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Pain from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Powder Springs
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasms Treatment in Powder Springs
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Powder Springs
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Restless Leg Syndrome Treatment in Powder Springs
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Powder Springs
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Powder Springs
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Powder Springs
- Tension Headaches Treatment in Powder Springs
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Trivisc Injections Treatment in Powder Springs
- Ulcerative Colitis Treatment in Powder Springs
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Urinary Incontinence Treatment in Powder Springs
- Vein Pain Treatment in Powder Springs
- Alpharetta
- Dacula
- Duluth
- Grayson
- Loganville
- Snellville
- Stone Mountain
- Atlanta
- Conyers
- Locust Grove
- McDonough
- Stockbridge
-
Texas
- Texas Pain Management
-
Waco
- Waco
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in Waco
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Waco
- Bone Bruise Treatment in Waco
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Waco
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Waco
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in Waco
- Treatment for Chronic Migraines and Headaches in Waco
- Cluster Headaches Treatment in Waco
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in Waco
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Waco
- Treatment for Crohn’s Disease in Waco
- Depression Pain Treatment in Waco
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Waco
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Waco
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in Waco
- Gout Pain Treatment in Waco
- Immunotherapy Treatment in Waco
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in Waco
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in Waco
- Joint Pain Treatment in Waco
- Knee Pain Treatment in Waco
- Long COVID Treatment in Waco
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in Waco
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in Waco
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Waco
- Neuragenex Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in Waco
- Non-Steroidal Alternative to Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Waco
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in Waco
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Waco
- Treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Pain in Waco
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Waco
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasms Treatment in Waco
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Waco
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Waco
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Waco
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Waco
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Waco
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Waco
- Restless Leg Syndrome Treatment in Waco
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Waco
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Waco
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Waco
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Waco
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Waco
- Tension Headaches Treatment in Waco
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Waco
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Waco
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Treatment in Waco
- Ulcerative Colitis Treatment in Waco
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Waco
- Urinary Incontinence Treatment in Waco
-
Victoria
- Victoria
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in Victoria
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Bone Bruise Treatment in Victoria
- Broken Bone Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Victoria
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Victoria
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in Victoria
- Treatment for Chronic Migraines and Headaches in Victoria
- Cluster Headaches Treatment in Victoria
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in Victoria
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Victoria
- Treatment for Crohn’s Disease in Victoria
- Depression Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Victoria
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in Victoria
- Gout Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Immunotherapy Treatment in Victoria
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in Victoria
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in Victoria
- Joint Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Knee Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Long COVID Treatment in Victoria
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in Victoria
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in Victoria
- Muscle Spasm Treatment Victoria
- Neuragenex Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in Victoria
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Pain in Victoria
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Victoria
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Victoria
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Victoria
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Tension Headaches Treatment in Victoria
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Victoria
- Arlington
- Azle
- Bedford
- Benbrook
- Burleson
- Crowley
- Euless
- Forest Hill
- Fort Worth
- Granbury
- Haltom City
- Hurst
- Keller
- Mansfield
- Mineral Wells
- North Richland Hills
- Richland Hills
- Saginaw
- Watauga
- Weatherford
- White Settlement
- Alice
- Aransas Pass
- Beeville
- Corpus Christi
- Ingleside
- Kingsville
- Portland
- Robstown
- Rockport
- Alamo Heights
- Balcones Heights
- Bergheim
- Blanco
- Boerne
- Bulverde
- Canyon Lake
- Castle Hills
- Cibolo
- Converse
- Garden Ridge
- Helotes
- Hollywood Park
- Kendalia
- Kirby
- Leon Valley
- Live Oak
- Marion
- New Braunfels
- Olmos Park
- San Antonio
- Schertz
- Selma
- Shavano Park
- Spring Branch
- Terrell Hills
- Timberwood Park
- Universal City
- Windcrest
- Big Sandy
- Daingerfield
- Diana
- East Mountain
- Gilmer
- Gladewater
- Hallsville
- Hawkins
- Jefferson
- Judson
- Kilgore
- Lone Star
- Longview
- Mount Pleasant
- New Diana
- Ore City
- Pittsburg
- Union Grove
- White Oak
- Winnsboro
- Balch Springs
- Forney
- Heartland
- Heath
- Mesquite
- Rockwall
- Sunnyvale
- Talty
- Terrell
-
Illinois
- Illinois Pain Management
-
Buffalo Grove
- Buffalo Grove Pain Management
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Bone Bruise Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Broken Bone Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment Buffalo Grove
- Cluster Headaches Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Crohn’s Disease Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Depression Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Gout Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Immunotherapy Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Joint Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Knee Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Long COVID Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Neuragenex Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in Buffalo Grove
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Non-Steroidal Alternative to Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Pain from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Restless Leg Syndrome Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Tension Headaches Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Buffalo Grove
-
New Lenox
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in New Lenox
- Allergy Testing in New Lenox
- Bone Bruise Treatment in New Lenox
- Carpal Tunnel Treatment in New Lenox
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in New Lenox
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in New Lenox
- Cluster Headache Treatment in New Lenox
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in New Lenox
- Crohn’s Disease Treatment in New Lenox
- Depression Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in New Lenox
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in New Lenox
- Gout Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Immunotherapy Treatment in New Lenox
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in New Lenox
- Joint Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Knee Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in New Lenox
- Migraines Headaches Treatment in New Lenox
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in New Lenox
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in New Lenox
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Pain from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in New Lenox
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in New Lenox
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Radial Tunnel Treatment in New Lenox
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in New Lenox
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Tension Headaches Treatment in New Lenox
- TMJ Pain Treatment in New Lenox
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in New Lenox
-
St. Charles
- Allergy Testing and Treatment in St. Charles
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Bone Bruise Treatment in St. Charles
- Broken Bone Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in St. Charles
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in St. Charles
- Chronic Fatigue Treatment in St. Charles
- Chronic Migraines and Headaches Treatment in St. Charles
- Cluster Headaches Treatment in St. Charles
- Combination Electroanalgesia Therapy Treatment in St. Charles
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in St. Charles
- Crohn’s Disease Treatment in St. Charles
- Depression Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in St. Charles
- Frozen Shoulders Treatment in St. Charles
- Gout Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Immunotherapy Treatment in St. Charles
- Interstitial Cystitis Treatment in St. Charles
- Joint Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Knee Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Long COVID Treatment in St. Charles
- Metabolic Dysfunction Treatment in St. Charles
- Muscle Spasm Treatment in St. Charles
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment in St. Charles
- Treatment for Pinched Nerve Pain in St. Charles
- Osteoarthritis Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Pain from Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in St. Charles
- Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment in St. Charles
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in St. Charles
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in St. Charles
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- TMJ Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in St. Charles
- Chicago
- Edgewater
- Evanston
- Gold Coast
- Hyde Park
- Lakeview
- Niles
- Park Ridge
- River North
- Skokie
- Arlington Heights
- Berwyn
- Brookfield
- Cicero
- Des Plaines
- Downers Grove
- Elk Grove Village
- Elmhurst
- Franklin Park
- Glenview
- Lombard
- Melrose Park
- Northbrook
- Oak Park
- Riverside
- Rosemont
- Schaumburg
- Westchester
- Wheeling
- Wilmette
-
Arizona
- Arizona Pain Management
- Ajo
- Benson
- Bisbee
- Green Valley
- Marana
- Naco
- Nogales
- Oro Valley
- Phoenix Valley
- Rio Rico
- Sahuarita
- San Simon
- Sasabe
- Tombstone
- Willcox
- Yuma
- Fountain Hills
- Gila Bend
- Rio Verde
- San Manuel
- Glendale
- Gold Canyon
- Maricopa
- Mammoth
- New River
- Paradise Valley
- Peoria
- Red Rock
- Picacho
- Queen Creek
- Oracle
- San Tan Valley
- Surprise
- Scottsdale
- Sun City
- Prescott
- Wickenburg
- Tonopah
- Wittmann
- Youngtown
-
Tucson
- Tucson Pain Management
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Tucson
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Tucson
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Tucson
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Tucson
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Tucson
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Tucson
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Tucson
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Tucson
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tucson
-
Waddell
- Waddel Pain Management
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Waddell
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Waddell
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Gout Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Joint Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Knee Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Waddell
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Waddell
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Waddell
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Waddell
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Waddell
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Waddell
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Waddell
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Waddell
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Waddell
- Vein Pain Treatment in Waddell
-
Arlington
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Arlington
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Arlington
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Arlington
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Arlington
- Vein Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arlington
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Arlington
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Arlington
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Arlington
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Joint Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Neuragenex NFPM Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Arlington
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Arlington
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Knee Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Gout Pain Treatment in Arlington
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Arlington
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Arlington
-
Avondale
- Avondale Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Avondale
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Avondale
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Avondale
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Avondale
- Vein Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Avondale
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Avondale
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Avondale
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Avondale
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Joint Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Neuragenex NFPM Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Avondale
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Avondale
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Knee Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Gout Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Avondale
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Avondale
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Avondale
-
Buckeye
- Buckeye Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Buckeye
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Buckeye
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Buckeye
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Buckeye
- Vein Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Buckeye
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Buckeye
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Buckeye
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Joint Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Neuragenex NFPM Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Buckeye
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Knee Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Gout Pain Treatment in Buckeye
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Buckeye
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Buckeye
-
Superior
- Superior Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Superior
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Superior
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Superior
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Superior
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Superior
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Superior
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Superior
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Superior
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Superior
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Superior
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Superior
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Superior
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Superior
- Vein Pain Treatment in Superior
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Superior
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Superior
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Superior
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Superior
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Superior
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Superior
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Superior
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Superior
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Superior
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Superior
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Superior
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Superior
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Superior
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Superior
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Superior
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Superior
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Superior
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Superior
- Joint Pain Treatment in Superior
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Superior
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Superior
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Superior
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Superior
- Gout Pain Treatment in Superior
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Superior
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Superior
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Superior
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Superior
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Superior
- Knee Pain Treatment in Superior
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Superior
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Superior
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Superior
-
Mesa
- Mesa Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Mesa
- IBS Treatment in Mesa
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Mesa
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Mesa
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Vein Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Mesa
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Tarsal Tunnel Treatment in Mesa
- Knee Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Mesa
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Gout Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Joint Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Mesa
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Mesa
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Mesa
-
Palo Verde
- Palo Verde Pain Management
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Palo Verde
- PAD Treatment in Palo Verde
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Vein Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Ankle Sprain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- IBS treatment in Palo Verde
- Knee Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Palo Verde
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Palo Verde
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Gout Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Palo Verde
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome treatment in Palo Verde
- Carpal tunnel treatment in Palo Verde
-
Morristown
- Morristown Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Morristown
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Morristown
- IBS Treatment in Morristown
- PAD Treatment in Morristown
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Morristown
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Morristown
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Morristown
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Morristown
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Morristown
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Morristown
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Morristown
-
Tempe
- Tempe Pain management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Tempe
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Tempe
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Vein Pain Treatment in Tempe
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Tempe
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Tempe
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Gout Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Tempe
- Joint Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Tempe
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Tempe
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Knee Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Tempe
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Tempe
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Tempe
-
Chandler
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Chandler Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Chandler
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Chandler
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Vein Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Chandler
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Chandler
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Chandler
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Joint Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Gout Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Chandler
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Knee Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Chandler
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Chandler
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Chandler
-
Anthem
- Anthem Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Anthem
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Anthem
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Anthem
- Vein Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Anthem
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Anthem
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Anthem
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Joint Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Anthem
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Anthem
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Knee Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Gout Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Anthem
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Anthem
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Anthem
-
Eloy
- Eloy Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Vein Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Joint Pain Treatment in Eloy, AZ
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Gout Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Eloy
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Eloy
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Knee Pain Treatment in Eloy
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Eloy
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Eloy
-
Florence
- Florence Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Florence
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Florence
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Florence
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Florence
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Florence
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Florence
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Florence
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Florence
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Florence
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Florence
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Florence
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Florence
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Florence
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Florence
- Vein Pain Treatment in Florence
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Florence
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Florence
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Florence
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Florence
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Florence
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Florence
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Florence
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Florence
- Joint Pain Treatment in Florence
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Florence
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Florence
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Florence
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Florence
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Florence
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Florence
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Florence
- Gout Pain Treatment in Florence
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Florence
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Florence
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Florence
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Florence
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Florence
- Knee Pain Treatment in Florence
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Florence
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Florence
-
Fort McDowell
- Fort McDowell Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Vein Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Joint Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Gout Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Knee Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Fort McDowell
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Fort McDowell
-
Phoenix
- Pain Management in Phoenix
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Phoenix
- Fibromyalgia Treatment in Phoenix
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Phoenix
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Phoenix
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Vein Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Phoenix
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Phoenix
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Phoenix
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Phoenix
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Joint Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Phoenix
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Gout Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Phoenix
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Phoenix
-
El Mirage
- El Mirage Pain management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in El Mirage
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in El Mirage
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in El Mirage
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Vein Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in El Mirage
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in El Mirage
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in El Mirage
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Joint Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Gout Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- TMJ Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Knee Pain Treatment in El Mirage
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in El Mirage
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in El Mirage
-
Coolidge
- Coolidge Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Coolidge
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Coolidge
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Coolidge
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Coolidge
- Vein Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Treatment for RLS in Coolidge, AZ
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Coolidge
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Coolidge I
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Coolidge
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Joint Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Gout Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Knee Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Coolidge
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Coolidge
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Coolidge
-
Gilbert
- Gilbert Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Gilbert
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Gilbert
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Gilbert
- Vein Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Gilbert
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Gilbert
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Gilbert
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Joint Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Gout Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Gilbert
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Knee Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Gilbert
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Gilbert
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Gilbert
-
Arizona City
- Arizona City Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Arizona City
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Arizona City
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Arizona City
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Arizona City
- Vein Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Arizona City
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Arizona City
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Arizona City
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Joint Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Arizona City
- Knee Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Gout Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Arizona City
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Arizona City
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Arizona City
-
Casa Grande
- Casa Grande Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Casa Grande
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Casa Grande
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Casa Grande
- Vein Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Casa Grande
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Casa Grande
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Casa Grande
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Joint Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Casa Grande
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Knee Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Gout Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Casa Grande
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Casa Grande
-
Casa Blanca
- Casa Blanca
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Vein Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Joint Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Knee Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Gout Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Casa Blanca
-
Aguila
- Aguila Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Aguila
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Aguila
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Aguila
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Aguila
- Vein Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Aguila
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Aguila
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Aguila
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Aguila
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Joint Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Neuragenex NFPM Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Aguila
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Aguila
- Knee Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Gout Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Aguila
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Aguila
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Aguila
-
Sacaton
- Sacaton Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Sacaton
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Sacaton
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Sacaton
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Vein Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Sacaton
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Sacaton
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Sacaton
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Sacaton
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Joint Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Sacaton
- Neuragenex NFPM Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Gout Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Knee Pain Treatment in Sacaton
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Sacaton
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Sacaton
-
Apache Junction
- Apache Junction Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Apache Junction
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Apache Junction
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Apache Junction
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Apache Junction
- Vein Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Apache Junction
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Apache Junction
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Apache Junction
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Joint Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Neuragenex NFPM Treatment For Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Apache Junction
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Knee Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Gout Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Apache Junction
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Apache Junction
-
Kearny
- Kearny
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Kearny
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Kearny
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Kearny
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Kearny
- Vein Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Kearny
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Kearny
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Kearny
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Kearny
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Joint Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Gout Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Kearny
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Kearny
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Knee Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Kearny
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Kearny
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Kearny
-
Stanfield
- Stanfield
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Stanfield
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Stanfield
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Stanfield
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Vein Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Stanfield
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Stanfield
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Stanfield
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Stanfield
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Joint Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Stanfield
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Gout Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Knee Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Stanfield
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Stanfield
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Stanfield
-
Goodyear
- Goodyear
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Goodyear
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Goodyear
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Goodyear
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Vein Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Goodyear
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Goodyear
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Goodyear
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Goodyear
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Joint Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Goodyear
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Gout Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Knee Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Goodyear
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Goodyear
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Goodyear
-
Litchfield Park
- Litchfield Park Pain Management
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Fibromyalgia Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Pain Medication Reduction Protocol Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Pain From Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Central Pain Syndrome Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Interstitial Cystitis Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Osteoporosis Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Bone Bruise Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Urinary Incontinence Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Frozen Shoulder Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Endometriosis Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Vein Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Postoperative Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Sleep Therapy Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Sciatica Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Non-Steroidal Alternative To Stellate Ganglion Blocks Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Ulcerative Colitis Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Restless Leg Syndrome Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- TriVisc Injections Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Phantom Limb Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Neck and Back Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Crohn’s Disease Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Compartment Syndrome Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Cluster Headache Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Chronic Migraines And Headache Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Joint Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Muscle Spasm-Induced Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Metabolic Dysfunction Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Long COVID Pain and Fatigue Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Pinched Nerve Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Gout Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Chronic Fatigue Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- TMJ Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Tension Headaches Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Tendonitis Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Knee Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Peripheral Neuropathy Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
- Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment in Litchfield Park
-
Alabama
- Alexander City
- Alabama Pain Management
- Andrew Jackson
- Bevelle
- Camp Hill
- Daviston
- Dadeville
- Dobbs
- Eclectic
- Elkahatchee Heights
- Elkahatchee Park
- Fuller
- Goodwater
- Hackneyville
- Hissop
- Hollins
- Indian Hills
- Jacksons Gap
- Kellyton
- Kowaliga
- Lake Hill Estates
- New Providence
- New Site
- Parish Hills
- Pearson Chapel
- Pinkneyville
- Reeves
- River Bend
- Rockford
- Santuck
- Sherwood Forest
- Sunny Level
- Tallassee
- Valley View
- Waverly
- Atmore
- Bay Minette
- Daphne
- Fairhope
- Flomaton
- Foley
- Gulf Shores
- Loxley
- Orange Beach
- Spanish Fort
- Stapleton
- Stockton
- Alaska
-
Arkansas
-
California
- California Pain Management
- Adelanto
- Alta Sierra
- Apple Valley
- Argus
- Bakersfield
- Barstow
- Barstow Heights
- Bodfish
- Boron
- Brown
- California City
- China Lake
- Desert View Highlands
- Edward Airforce
- Elk Mills
- Elkton
- Fort Irwin
- Fort Mitchell
- Glenwood
- Golden Hills
- Independence
- Inyokern
- Johannesburg
- Kernville
- Lake Isabella
- Lake Los Angeles
- Lancaster
- Leona Valley
- Little Elm
- Loma Linda
- Lone Pine
- Mojave
- Oakley
- Oildale
- Palmdale
- Pearsonville
- Red Mountain
- Randsburg
- Ridgecrest
- Rosamond
- Searles Valley
- Searless Valley
- Tehachapi
- Trona
- Victorville
- Weldon
- Wofford Heights
- Agoura Hills
- Calabasas
- Encino
- Malibu
- Oak Park
- Thousand Oaks
- Topanga
- Westlake Village
- Woodland Hills
- Anaheim
- Artesia
- Brea
- Buena Park
- Cerritos
- Cypress
- Fullerton
- Garden Grove
- Irvine
- La Habra
- La Mirada
- La Palma
- Placentia
- Santa Ana
- Stanton
- Whittier
- Antioch
- Brentwood
- Byron
- Concord
- Danville
- Discovery Bay
- Livermore
- Martinez
- Mountain House
- Pittsburg
- Pleasant Hill
- Rio Vista
- San Ramon
- Stockton
- Tracy
- Walnut Creek
- Carolina
- Connecticut
- Delaware
-
Florida
- Florida Pain Management
- Altamonte Springs
- Apopka
- Belle Isle
- Celebration
- Clermont
- Eustis
- Groveland
- Kissimmee
- Lake Buena Vista
- Leesburg
- Longwood
- Maitland
- Mount Dora
- Ocoee
- Orlando
- Oviedo
- Pine Hills
- Sanford
- Windermere
- Winter Park
- Winter Springs
- Winter Garden Florida
- The Villages
- Attapulgus
- Crawfordville
- Havana
- Lloyd
- Midway
- Monticello
- Quincy
- St. Marks
- Tallahassee
- Woodville
- Hawaii
-
Idaho
-
Indiana
- Indiana Pain Management
- Akin Park
- Boonville
- Chandler
- Chrisney
- Dale
- Darmstadt
- Elberfeld
- Evansville
- Fort Branch
- Haubstadt
- Haynie's Corner Arts District
- Henderson
- Huntingburg
- Jacobsville
- Jasper
- Lamasco
- Lynnville
- Madisonville
- Melody Hill
- Morganfield
- Mount Vernon
- New Harmony
- Newburgh
- North Park
- Oakland City
- Owensboro
- Petersburg
- Poseyville
- Princeton
- Providence
- Rockport
- Santa Claus
- Tell City
- Wadesville
-
Iowa
-
Kansas
- Kentucky
-
Louisiana
- Louisiana Pain Management
- Albany
- Baker
- Baton Rouge
- Central
- French Settlement
- Gonzales
- Holden
- Killian
- Livingston
- Maurepas
- Port Vincent
- Satsuma
- Shenandoah
- Springfield
- Walker
- Watson
- Zachary
- Amite City
- Bogalusa
- Covington
- Denham Springs
- Franklinton
- Hammond
- Independence
- Kenner
- Kentwood
- Madisonville
- Mandeville
- Ponchatoula
- Roseland
- Tickfaw
- Maine
-
Maryland
- Massachusetts
-
Michigan
- Michigan Pain Management
- Ada
- Allendale
- Ann Arbor
- Byron Center
- Cascade Township
- Coopersville
- Dearborn
- Detroit
- East Grand Rapids
- Grand Haven
- Grand Rapids
- Grand Rapids Michigan
- Grandville
- Holland
- Hudsonville
- Kentwood
- Lansing
- Lowell
- Muskegon
- Rockford
- Sparta
- Sterling Heights
- Walker
- Wayland
- Warren
- Zeeland
- Alto
- Belmont
- Belding
- Caledonia
- Cannonsburg
- Cascade
- Cedar Springs
- Clarksville
- Comstock Park
- Cutlerville
- Dorr
- Forest Hills
- Greenville
- Hastings
- Ionia
- Jenison
- Lake Odessa
- Marne
- Middleville
- Saranac
- Wyoming
- Northview
-
Rhode Island
- Rhode Island Pain Management
- Arlington
- Attleboro
- Barrington
- Blackstone
- Bristol
- Central Falls
- Coventry
- Cranston
- Cumberland
- Dartmouth
- East Greenwich
- East Providence
- East Taunton
- Fall River
- Johnston
- Lincoln
- Middletown
- Millville
- Narragansett
- North Kingstown
- North Providence
- North Scituite
- Pawtucket
- Portsmouth
- Providence
- Rehoboth
- Scituite
- Seekonk
- Smithfield
- Swansea
- Tiverton
- Warwick
- Warren
- West Warwick
- Westport
-
Minnesota
-
Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
-
Nevada
- New Hampshire
-
New Jersey
-
New Mexico
- New York
-
North Carolina
- North Carolina Pain Management
- Atkinson
- Boiling Spring Lakes
- Bolivia
- Burgaw
- Calabash
- Carolina Beach
- Charlotte
- Castle Hayne
- Hampstead
- Holly Ridge
- Kure Beach
- Leland
- Navassa
- Oak Island
- Rocky Point
- Shallotte
- Southport
- Surf City
- Topsail Beach
- Wilmington
- Wrightsville Beach
- Sneads Ferry
- Ogden
- Porters Neck
- Figure Eight Island
- Scotts Hill
- Murrayville
- North Dakota
-
Ohio
- Ohio Pain Management
- Anna
- Bellefontaine
- Botkins
- Celina
- Cridersville
- Delphos
- Fort Loramie
- Jackson Center
- Lima
- Minster
- New Bremen
- Piqua
- Sidney
- St. Marys
- Troy
- Uniopolis
- Van Wert
- Wapakoneta
- Waynesfield
- Burkettsville
- Chickasaw
- Coldwater
- Fort Recovery
- Greenville
- Maria Stein
- Mendon
- Montezuma
- Rockford
- Rossburg
- St. Henry
- Union City
- Versailles
- Oklahoma
-
Pennsylvania
- Pennsylvania Pain Management
- Doylestown
- Warminster
- Warrington
- Horsham
- Willow Grove
- Ashley
- Benton
- Berwick
- Bloomsburg
- Dallas
- Forty Fort
- Glen Lyon
- Hunlock Creek
- Kingston
- Mountain Top
- Nanticoke
- Orangeville
- Plymouth
- Shickshinny
- Stillwater
- Sugar Notch
- Sweet Valley
- Wapwallopen
- Wilkes-Barre
- Allentown
- Bath
- Bethlehem
- Catasauqua
- Center Valley
- Easton
- Emmaus
- Nazareth
- Northampton
- Quakertown
- Whitehall
- South Carolina
-
South Dakota
-
Tennessee
- Tennessee Pain Management
- Ashland City
- Bellevue
- Brentwood
- Franklin
- Gallatin
- Goodlettsville
- Hendersonville
- Hermitage
- Murfreesboro
- Nashville
- Nolensville
- Apison
- Chattanooga
- Cleveland
- Collegedale
- East Brainerd
- East Ridge
- Fort Oglethorpe
- Harrison
- Hixson
- Lookout Mountain
- Red Bank
- Ringgold
- Signal Mountain
- Soddy-Daisy
-
Utah
- Utah Pain Management
- Alpine
- American Fork
- Benjamin
- Bluffdale
- Cedar Fort
- Cedar Hills
- Draper
- Eagle Mountain
- Elk Ridge
- Genola
- Goshen
- Highland
- Lake Shore
- Lehi
- Lindon
- Mapleton
- Orem
- Palmyra
- Payson
- Pleasant Grove
- Provo
- Salem
- Santaquin
- Saratoga Springs
- Spanish Fork
- Springville
- Vineyard
- Wallsburg
- Woodland Hills
- Vermont
-
Virginia
- Virginia Pain Management
- Aydlett
- Barco
- Camden
- Coinjock
- Corolla
- Currituck
- Duck
- Edenton
- Elizabeth City
- Grandy
- Hertford
- Kill Devil Hills
- Kitty Hawk
- Manteo
- Moyock
- Nags Head
- Shiloh
- South Mills
- Southern Shores
- Wanchese
- Alexandria
- Hampton Roads
- Smithfield
- Carrollton
- Isle of Wight
- Battery Park
- Ashland
- Beaverdam
- Bon Air
- Chester
- Chesterfield
- East Highland Park
- Fort Lee
- Goochland
- Highland Springs
- Hopewell
- Lakeside
- Laurel
- Maidens
- Mechanicsville
- Richmond
- Sandston
- Short Pump
- Tuckahoe
- Varina
- Altavista
- Amherst
- Appomattox
- Bedford
- Concord
- Elon
- Gretna
- Huddleston
- Hurt
- Lynchburg
- Madison Heights
- Moneta
- Montvale
- Rustburg
- Timberlake
- Accomac
- Assawoman
- Atlantic
- Belle Haven
- Birdsnest
- Bloxom
- Cape Charles
- Capeville
- Cheriton
- Chincoteague
- Craddockville
- Davis Wharf
- Eastville
- Exmore
- Franktown
- Greenbackville
- Greenbush
- Hacksneck
- Hallwood
- Harborton
- Horntown
- Jamesville
- Jenkins Bridge
- Keller
- Lee Mont
- Locustville
- Machipongo
- Mappsville
- Marionville
- Mears
- Melfa
- Modest Town
- Nassawadox
- Nelsonia
- New Church
- Oak Hall
- Onancock
- Onley
- Oyster
- Painter
- Parksley
- Pocomoke City
- Princess Anne
- Pungoteague
- Quinby
- Salisbury
- Sanford
- Saxis
- Seaview
- Snow Hill
- Tangier
- Tasley
- Temperanceville
- Townsend
- Wachapreague
- Wallops Island
- Wardtown
- Wattsville
- Weirwood
- Willis Wharf
- Withams
-
Washington
- Washington Pain Management
- Blyn
- Carlsborg
- Chimacum
- Gardiner
- Indian Island
- Joyce
- Marrowstone Island
- Port Angeles
- Port Angeles East
- Port Hadlock-Irondale
- Port Ludlow
- Port Townsend
- Quilcene
- Sequim
- Airway Heights
- Cheney
- Colbert
- Fairchild Air Force Base
- Liberty Lake
- Medical Lake
- Millwood
- Nine Mile Falls
- Otis Orchards
- Spokane
- Spokane Valley
- West Virginia
- Wyoming
-

