Experiencing a bone fracture is undeniably a defining and challenging time. It causes immediate pain, which might persist for weeks or even months during the healing process. Fractures also limit your mobility and ability to carry out daily activities. And, beyond the physical discomfort, they can become a predominant source of concern, affecting your emotional and mental well-being.
Whether the fracture was caused by a sudden accident, injury, overuse, or an underlying health issue, having an in-depth understanding is essential for effectively managing discomfort and optimizing recovery.
This article aims to provide valuable insights into all the nuances of bone fractures. We’ll explore the various types and causes, highlighting the symptoms and potential complications. We’ll also discuss the clinical process of assessing a bone fracture and the various treatment options available.
Additionally, we explore how the healing process from a bone fracture can be both effective and more comfortable, thanks to the innovative treatments offered by RELATYV Mobile Pain Management. Our protocols are specially designed to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with a broken bone without resorting to long-term painkillers or invasive surgical procedures.
Let’s begin by learning more about the many types of bone fractures.
What Is A Bone Fracture?
A bone fracture occurs when a bone is damaged or broken. It usually leads to a sudden and potentially ongoing disturbance of its normal structure and function until it is treated and healed. The immediate consequence is pain, and a fracture can range from a very small hairline crack to a complete break.
There are many other types of bone fractures, each one bringing its own set of challenges.
Different Types Of Fractures
It’s important to recognize that not all bone fractures are the same and that their nature and severity will determine the course of treatment and overall recovery. Let’s explore the different types in the headings below.
Closed
A closed fracture, also known as a “simple” fracture, occurs when the bone is damaged, yet there’s no penetration through the skin. The good news is that this type of fracture is generally less complicated to treat. However, it still requires careful management to ensure the bone realigns properly during the healing process.
Open
On the other hand, an open or “compound” fracture occurs when the bone breaks through the skin, becoming visible. Due to the nature of this kind of fracture, there is an increased chance of infection and tissue damage. Immediate and specialized care is crucial for open fractures to ensure proper treatment and minimize potential complications.
Incomplete
An incomplete, or “partial” fracture, develops when the bone is partially broken but not completely separated. This subset also includes greenstick fractures in children, where the bone bends but doesn’t break entirely. While the nature of these fractures may seem less severe, they require a highly involved treatment plan to ensure the bone heals in alignment and without deformity.
Complete
A complete fracture indicates a total break through the bone, resulting in two or more distinct pieces. When a complete fracture becomes “displaced,” it means the broken bone has moved out of proper alignment.
Beyond these broad categories, fractures are also named based on the pattern of the break, how the break looks, and what direction it’s broken, such as:
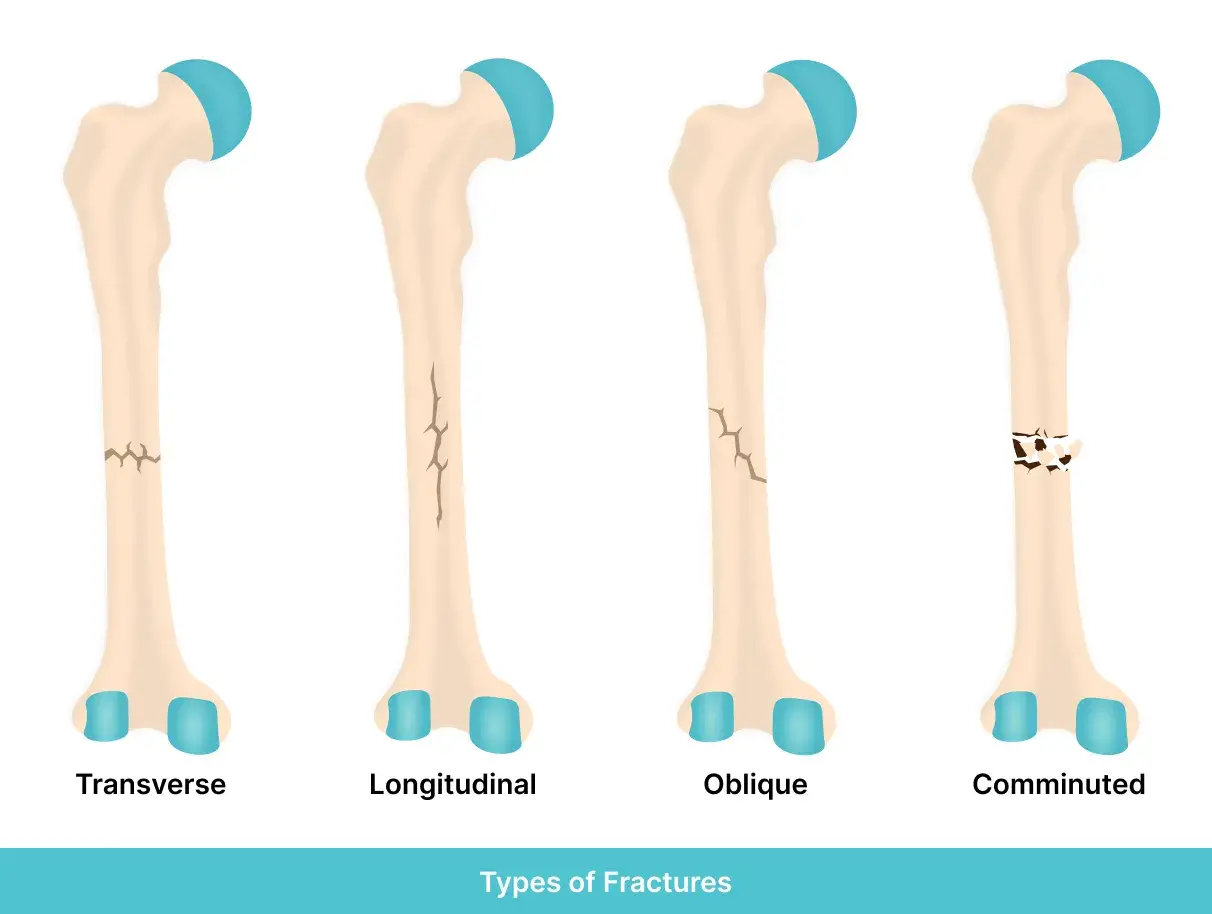
Transverse
When a fracture is referred to as “transverse,” it implies that the break occurred exactly across its axis. This type of fracture often results from a direct impact.
Longitudinal
Alternatively, a longitudinal fracture is a break that runs parallel to the bone’s axis. While they’re less common in general, they are typically seen in long bone fractures, such as the femur.
Comminuted
Comminuted fractures are much more complex, involving the bone breaking into multiple fragments. This poses a much higher risk of complications during healing, and in many cases, surgical intervention is needed to restore stability and function.
Oblique
An oblique fracture is differently patterned again, describing a diagonal break across the bone. This type of fracture is often caused by a twisting or angular force.
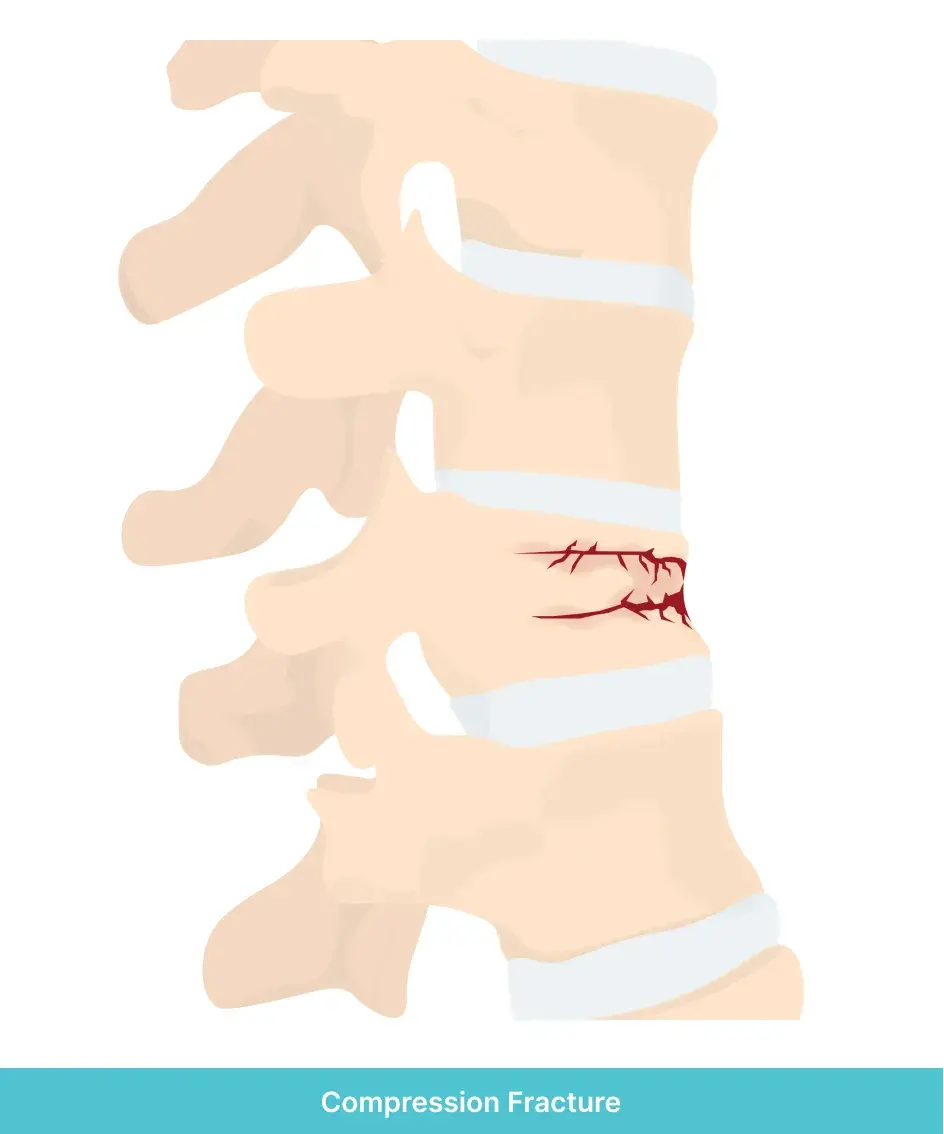
Compression
Finally, compression fractures are frequently seen in the spine, where the
vertebrae are crushed or collapsed. This can be caused by injury or osteoporosis but is usually due to
age-related degeneration. This condition usually leads to a forward-leaning “stooped” posture in older
adults.
While an open fracture and some complete fractures may be unmistakable, it’s not
always so clear whether a bone has been broken. Let’s move on to how individuals can identify bone pain and
the typical symptoms of fractures.
Recognizing A Fracture - Bone Pain And Other Symptoms
Pain is a very personal and subjective experience. This means that different people will experience varying levels of pain from bone fractures, and no particular type is inherently more painful than another.
In addition to this, bone pain can generate symptoms that are similar to other musculoskeletal conditions, like a sprained ankle, plantar fasciitis, or tendonitis, making them difficult to detect. Pain can feel like a deep ache, sharp pains, extreme tenderness, or pinching.
Aside from pain, there are additional symptoms that serve as telltale signs you may have fractured a bone. These include:
Swelling, Redness, Or Bleeding
Bone fractures can cause symptoms of swelling and redness. This is a sign of the natural healing process, inflammation – the body’s initial response to injury. After the incident, the immune system immediately sends cells to remove damaged tissue, bone fragments, and blood from broken vessels.
The inflammation process then attracts more immune cells, increasing blood flow to the area. This is what causes the injured area to appear inflamed, red, swollen, and tender. In severe cases of open or compound fractures, there can be external bleeding.
Restricted Mobility
Experiencing restricted mobility and reduced function is a notable symptom of a bone fracture. Difficulty moving a limb or joint can be due to the break itself, tissue damage, pain, and swelling.
However, some people are able to keep moving a fractured bone, but just because there is mobility of the affected area doesn’t mean there is no fracture.
Broken Skin With Protruding Bone
Open fractures are serious. When a bone breaks through the skin and protrudes outward, it is a clear indication that the fracture requires immediate medical attention.
Crepitus Of Bone Fragments
Bone crepitus describes the grating or cracking sensation during movement that can accompany fractures. Recognizing this specific symptom as a potential bone fracture can guide individuals to seek an accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
We encourage you to listen to your body’s signals. If you experience bone pain or other signs that something isn’t right, it’s your body urging you to stop and seek medical attention. Quick recognition and timely intervention are key to preventing further damage and guiding an effective treatment strategy.
Crepitus
Crepitus, which is the term used for the grating sensation that affects your joints, often indicates a more significant underlying problem. It is the crunching, cracking, or popping sound and sensation felt when your joints move. It can be caused by...
Common Causes Of Bone Fractures
Bone fractures can happen to anyone at any time. Although accidents and sports injuries are typical causes, fractures can occur for a range of reasons. Let’s look at some of the more common ones under the headings below:
Trauma Or Injury
Accidents happen to all of us. Falls, sports-related impacts, or vehicle accidents all have the potential to cause fractures. If you’ve experienced any trauma or injury and have symptoms of pain or other signs that you may have broken a bone, it’s vital to seek prompt medical attention.
Overuse Or Repetitive Forces
When repetitive force is placed on the bones, it can result in small fractures on the bone’s surface, described as stress fractures. People who engage in physical activities, such as athletes or individuals with physically demanding jobs, are more susceptible. These fractures are known to be quite painful and also contribute to a reduction in structural integrity.
Older individuals who begin exercising more regularly than in the past, either to stay fit or as part of a therapeutic regimen for a specific health concern, may also develop stress fractures.
Health Conditions
A number of medical conditions have the potential to weaken bones and raise the risk of bone fractures. These include but are not limited to:
Osteoporosis
This condition is common in older individuals. It weakens bones by reducing bone density, making them thinner and more fragile. This is due to a reduction in new bone formation and makes them prone to fractures.
Bone Cancer
Bone cancer that originates in the bone itself, also known as a bone sarcoma, isn’t very common. It is more common to see cancers that have originated elsewhere and spread to the bones. Either way, developing cancer in the bone will seriously affect its integrity and is a serious risk factor for fractures.
Hyperparathyroidism
Overactivity of the parathyroid glands causes the production of too much parathyroid hormone, which can weaken bones over time. It does this by causing your bones to release too much calcium, leaving them brittle and susceptible to fractures.
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)
This genetic disorder is aptly termed “brittle bone disease.” It is caused by a defect in the genes responsible for producing bone-strengthening collagen. As a result, bones develop with a weakened structure, making them fragile and prone to fracturing easily, even with little to no apparent injury.
In addition to these common causes, several lifestyle factors can increase the risk of bone fractures. We’ll discuss these in more detail in the next section.
Risk Factors Associated With Fractures
Learning about the factors that increase the likelihood of bone fractures can lead you to proactively improve your overall bone health. Let’s look at the following risk factors:
- Age: As we age, the bones tend to weaken naturally due to a reduction in new bone formation, making them more susceptible to fractures.
- Gender: Women, especially those who are postmenopausal, face an elevated risk of bone fractures because reduced estrogen levels can impact bone density.
- Reduced bone density: Reduced bone density, whether due to aging, medical conditions like osteoporosis, or lifestyle factors, weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures.
- Smoking: The use of tobacco directly affects bone health by causing reduced bone mass. This increases a person’s vulnerability to developing osteoporosis and fractures.
- Alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol long term is also known to weaken bones over time, making fractures more likely.
- Calcium and vitamin D deficiency: Adequate vitamin D levels are vital for optimal calcium absorption in the body. An insufficient intake of both of these essential nutrients compromises bone strength and elevates the risk of fractures.
Now that you know the symptoms, common causes, and associated risk factors of bone fractures, you can make more informed choices about your lifestyle and recognize when to seek medical attention.
Remember, your health is a priority, and there’s always support and guidance available for you. Let’s change our focus to discuss the clinical process of assessing a bone fracture, as well as the various treatment options available.
Which Examinations Identify Bone Fractures?
When doctors suspect a bone fracture, they may order diagnostic tests to precisely identify and assess the bone and surrounding tissues. The following tests provide health professionals with important information about the extent of the injury:
X-Rays
X-rays are used frequently because they can provide clear and detailed images of the bones’ structure. A simple X-ray will often be enough for your radiologist and doctor to decipher information such as which bone is broken, where, and what type of fracture has occurred.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
An MRI is a powerful tool that goes beyond bones, offering detailed insights into soft tissues like muscles, ligaments, cartilage, and tendons. It becomes especially useful when symptoms might indicate soft tissue damage or if a severe fracture has potentially affected the surrounding structures.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
CT scans are a special type of X-ray imaging that takes cross-sectional pictures, providing a 3-D image rather than the X-ray’s 2D image. As a result, CT scans can provide a more comprehensive view of the injury from different angles, allowing specialists to evaluate both complex and small stress fractures, as well as identify potential complications.
Once a fracture is formally assessed, healthcare professionals can develop tailored treatment plans that support your journey to optimal healing, helping you return to your normal daily routine. In the upcoming sections, we’ll underscore why receiving this timely medical assessment is so important.
The Importance Of Prompt Medical Care For Fractures
Seeking prompt medical attention and care for fractures is crucial. This is because it can significantly influence an individual’s overall recovery and well-being. Let us explain this further.
Early intervention is going to ensure the fracture is accurately diagnosed and appropriately treated, improving the chances of successful healing. Without treatment, fractures can lead to complications like misalignment, deformity, and stress on surrounding muscles and nerves, resulting in heightened pain, reduced mobility, and long-term damage.
Additionally, if treatment is delayed, these complications may require multiple surgeries. However, even with surgical intervention, there is no guarantee full mobility and function can be restored.
Beyond physical discomfort, the long-term effects of not addressing fractures can impact a person’s mental health and overall quality of life. In the next section, we will discuss more about the acute and severe issues that may arise.
How Untreated Bone Fractures Can Lead to Serious Complications
Serious complications from untreated bone fractures can manifest within hours to days of the incident. This includes issues of blood loss, ongoing damage to surrounding tissues and organs, and infections that might affect the bone or even spread to the bloodstream, leading to sepsis.
Timely intervention for symptoms of a potential fracture is crucial to prevent these complications from escalating. Recognizing the urgency in treating fractures could prevent you from experiencing prolonged pain, potential disability, and the need for additional medical procedures.
A range of treatment options is available for managing the pain and discomfort of a bone fracture that also supports healing and ensures a smoother recovery. Keep reading to learn more.
Conventional Treatment Options For Bone Fractures
The treatment choices for bone fractures will depend on individual factors like fracture severity, underlying health conditions, and personal preferences. To keep it simple, we’ll break down the different treatment options in the headings below:
Medication
Doctors often prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatories, such as ibuprofen, to manage pain and swelling during recovery. Over-the-counter options may not be enough in certain situations, and a doctor might suggest stronger prescription pain relievers to keep you comfortable.
Immobilization
In many cases, keeping the injured bone still helps it re-align correctly, ensuring it regains strength and works well once it’s healed.
- Splint – A splint provides external support and prevents movement in the affected area.
- Brace – Braces are more rigid than splints and offer enhanced stability for fractures that require a more secure setting.
- Cast – Casts, made of plaster or fiberglass, provide comprehensive support. They aim to completely immobilize and stabilize the fractured bone during the healing process.
- Slings – Slings support and immobilize the arm, facilitating healing for certain upper body fractures.
Traction
Traction is a more involved treatment that typically requires you to stay in the hospital for appropriate care. It involves the application of a gentle pulling force to realign and immobilize bones, which is particularly useful for fractures of the hips and lower legs.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is beneficial for minor fractures or as part of aftercare for larger fractures. It involves exercises and stretches that help restore mobility, strength, and flexibility. This provides additional and ongoing support after the initial healing phase.
Bone Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be recommended for treatment.
Internal Fixation
Internal fixation surgery involves implants like screws, plates, or rods to stabilize fractures. This aims to promote proper alignment and healing.
External Fixation
External fixation involves using an external frame to stabilize bones from the outside. This is typically used in highly complex fractures and requires additional surgeries for removal as healing progresses.
Surgery should always be considered a last-resort treatment option and only be utilized when all other treatments are deemed unviable. This is because any invasive surgical procedure is regarded as a high-risk treatment with increased risks of complications.
After exploring these treatment options, the next step is to understand the recovery process.
How Long It Takes To Recover From Fractures
The actual bone break is a singular event, but the recovery journey will vary from person to person. The specific timeline depends on factors like the fracture’s severity and individual health conditions.
As a guide, minor fractures may mend in a few weeks, while complex ones could take months to a year. For a speedy recovery, it’s important to follow your doctor’s treatment plan and make sure your pain is well managed.
Effectively managing pain is a key component of healing. This is because the stress response to pain can hinder the recovery process. So, having effective pain control not only boosts your overall comfort but can also contribute to a more efficient recovery and improve your overall clinical outcome.
But this shouldn’t mean taking more or stronger pain medications. In the next section, we’ll discover the RELATYV Mobile Pain Management protocol for pain management and how its innovative approach helps support adequate pain relief and accelerate the recovery process without needing to take more pills.
Our Protocol For Pain Management And Rapid Recovery From Fractured Bones
We offer an innovative approach to pain management known as RELATYV Mobile Pain Management. This tailored method prioritizes overall well-being, aiming to enhance daily functioning and provide effective tools for individuals to manage ongoing pain and discomfort.
Our comprehensive protocol is proudly non-pharmaceutical, non-chiropractic, and non-surgical, incorporating the below therapies:
Electroanalgesia
Electroanalgesia is a pain management technique that uses high-pulse electrical current to ease pain, boost blood circulation, improve mobility, and induce...
IV Therapy
IV nutritional therapy, or intravenous therapy, involves administering vital nutrients directly to the bloodstream through an IV. This type of treatment bypasses the digestive system, allowing for maximum absorption and utilization of nutrients by the...
Lifestyle Counseling
Lifestyle counseling is an approach to managing chronic pain that involves identifying, assessing, and modifying lifestyle factors contributing to an individual's pain. For example, lifestyle factors such as nutrition, physical activity, stress, sleep quality...
Enhance Bone Strength Through Accelerated Healing
Understanding bone fractures is crucial to ensuring effective treatment and the best potential outcome. Whether dealing with minor or complex fractures, recognizing symptoms, seeking prompt medical care, and adopting appropriate treatments contribute to a smoother healing journey.
While recovery timelines can vary between individuals, encouraging optimal recovery for long-term bone health is key. Managing pain is a crucial part of the bone healing process, influencing both comfort and efficiency.
The RELATYV Mobile Pain Management protocol provides effective pain management without pharmaceuticals or surgery. This whole-person approach prioritizes overall well-being, ensuring a comfortable and potentially accelerated healing process.
Remember, there’s no need to endure constant discomfort as your body heals from a fracture. With RELATYV Mobile Pain Management, we are dedicated to providing you with pain relief that makes your healing journey smoother and ensures you can recover with confidence and ease.
Looking for a way to speed up the healing of broken bones?