Did you know that the peroneal nerve, also known as the fibular nerve, conveys crucial messages between your brain and your lower legs, feet, and toes? In fact, this is such an important nerve that if it becomes dysfunctional, all of the orchestrated movements and sensations of your lower extremities can become disrupted.
With this article, we hope to clearly define peroneal nerve dysfunction and explore the consequences that can manifest when it is negatively impacted, including the wide range of potential symptoms. We will also uncover the known risk causes of this debilitating condition and share the potential impact it can have on daily life for those affected.
Additionally, we will provide some insights into how health professionals test for and diagnose peroneal nerve dysfunction, as well as the available treatment options, ranging from conventional medicine to surgical interventions.
Additionally, we will share how the revolutionary Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management techniques can specifically address the painful symptoms of nerve dysfunction, offering hope to individuals in finding effective and lasting pain management solutions.
Let’s start by exploring the fascinating anatomy of the peroneal nerve to provide you with a fundamental understanding of the vital role it plays in your body.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Peroneal Nerve
The peroneal nerve is unique in that it originates directly from where the sciatic nerve ends in your thigh, known as the common peroneal nerve. This first nerve branch delivers crucial messages for movement and sensation to the lower leg muscles, especially the large hamstring (bicep femoris) at the back of your leg.
As the common peroneal nerve travels around the outside of the knee, it splits into two separate branches known as the deep peroneal nerve and the superficial peroneal nerve. The deep branch specifically delivers messages to the muscles at the front of the leg (tibia), while the superficial branch targets the muscles on the side of the leg (fibula). Both the deep and superficial branches extend their messages all the way down to the top of the foot.
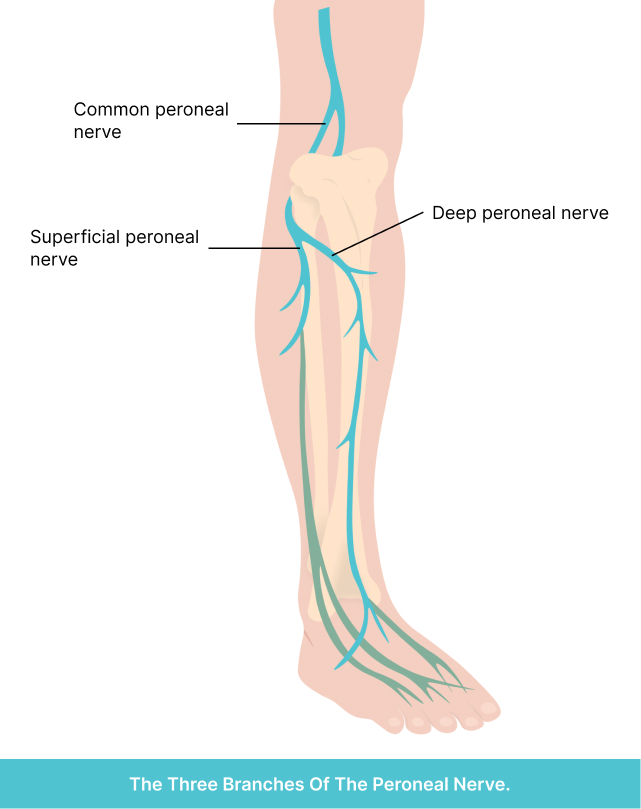
You can see how all three branches of the peroneal nerve act as important conductors for the major lower leg muscles, enabling movements like pointing your foot up and turning it outward. Although we might consider these movements very basic actions, it’s truly remarkable just how vital these nerves are for maintaining your everyday stability and balance and ensuring smooth muscle coordination throughout your lower legs and feet.
In a nutshell, the peroneal nerve, with its common, superficial, and deep branches, is essential for walking, standing, and maintaining balance. It’s a power player behind your ability to lead an active and mobile life. Understanding its role is key to realizing how peroneal nerve dysfunction can impact your overall mobility and well-being.
Now, let’s shift our focus to discuss what happens when the peroneal nerve becomes dysfunctional and the impact it can have on an individual’s quality of life.
What Is Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction?
Peroneal nerve dysfunction is a type of neuropathy (peripheral nerve damage) that indicates nerve damage stemming from an injury or disease. When this important nerve becomes harmed, it can create a chain reaction, disrupting the crucial network of nerve impulses between your brain and your lower legs and feet.
As a consequence, disruption of the peroneal nerve can lead to blocked or inappropriate nerve signals being triggered, profoundly impacting the lower leg’s ability to function normally.
Furthermore, if it is left untreated, peroneal nerve damage and dysfunction can cause chronic pain and inflammation in the affected leg, causing a number of challenging or distressing symptoms. For example, you may develop muscle weakness and reduced limb movement, as well as sensory disturbances like tingling, numbness, stabbing or aching pains, or varying hot or cold sensations.
In severe cases, peroneal nerve dysfunction can impact your ability to accomplish even the simplest of tasks due to the associated pain and muscle weakness. A reduction of overall mobility can impact your ability to have an active lifestyle and potentially lead to isolation and declines in mental health and overall well-being.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial information if you are dealing with peroneal nerve dysfunction. It shows how important it is to seek professional care for tailored management and support so you can find strategies to improve your quality of life. In the next section, we will discuss the various symptoms of this complex condition in more detail.
Symptoms Of Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction
It’s important to recognize that symptoms of peroneal nerve dysfunction will vary from person to person, presenting in a range of different ways, each with its unique challenges.
This section will examine some of the more prevalent symptoms and go into further detail about the potential effects they may have on your life.
Difficulty In Walking Or Moving
The disrupted nerve signaling of peroneal nerve dysfunction can significantly impact your ability to walk or move the affected leg comfortably. This can simply be from poor sensation or may be due to muscle weakness, impacting the ability of the foot to point upwards and rotate, otherwise known as ‘foot drop’.
As a result, you may face challenges like limping, stumbling, and instability, which increases the risk of falls and overall mobility decline. Even the simplest of daily activities, such as getting out of bed in the morning, can be negatively impacted.
Pain In The Lower Leg or Foot
A peroneal nerve injury can bring with it painful symptoms that present in varying degrees of intensity. It is normal for sufferers to experience sharp, shooting pains, aching discomforts, or a persistent throbbing sensation in the foot or lower leg.
Each person’s pain will be different in terms of its location and intensity, which will have varying effects on their everyday activities and overall quality of life.
Numbness, Tingling, Or Loss Of Sensation
Any nerve impairment will often lead to sensations of numbness, tingling, or, in severe cases, a complete loss of sensation in the affected areas. In the case of peroneal nerve dysfunction, this can feel like pins and needles, a lack of responsiveness to touch, or strange feelings of heat or cold down the leg.
When your normal sensations become compromised, it might affect how well you interact with your surroundings, such as not noticing cuts or bruises, which may lead to infections or other complications.
Lower Leg Muscle Loss
In long-standing, severe cases of peroneal nerve dysfunction, a more notable consequence is when muscle mass begins to decline. As the nerve fails to send signals, the muscles it normally sends messages to become overly passive and begin to shrink as a result of the lack of movement.
Not only can this result in a loss of muscle strength and mass, but it can also visibly alter the way the muscles look and even alter the normal contours of the leg.
Understanding the symptoms of peroneal nerve dysfunction is helpful for you to gauge the severity of your own condition. This knowledge can empower you to make informed decisions about managing uncomfortable symptoms, reducing their impact on your daily life, and preventing your condition from worsening.
Next, we’ll look into the potential causes and recognized risk factors of this impactful condition.
Difficulty In Walking
Difficulty in walking is one of the most common types of disability in the US. According to reports, around 7% of Americans seriously struggle with walking or climbing stairs. This figure is much lower for people aged 18-34 (1%), but much higher for older...
Chronic Foot Pain
Dealing with chronic foot pain is debilitating enough as it is. After all, our feet are an essential part of our everyday lives, and any pain that interferes with their proper functioning can disrupt our daily activities. Many people attempt to treat foot...
Sensation Of Numbness
Feeling a numbness in your body can be a scary and uncomfortable experience. This numbness, also known as paresthesia, is a tingling or prickling sensation that can occur anywhere in the body. It is often described as feeling like pins and needles or a loss...
Muscle Tenderness
Have you been experiencing muscle tenderness lately? Perhaps you’re feeling tension and discomfort around your neck, shoulders, lower back, hips, or legs. While most muscle discomfort is not too disruptive, if it worsens, it can start impacting your daily...
Pins And Needles
Everyone experiences paresthesia at least once in their lives. Think, for example, of when you’ve been sitting cross-legged for too long and you have the sensation that your limb has “fallen asleep.” Or it can happen while you are asleep, often because...
Tingling Sensation in Hands and Feet
Paresthesia is the medical term to describe a tingling sensation in parts of the body, most notably in the hands or feet. It can manifest as a prickling feeling, numbness, burning, and shooting pain. Although these sensations are usually harmless, they can...
Lower Leg Muscle Loss
Muscle atrophy is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Although there are many different reasons why muscles begin to atrophy, it also tends to happen naturally, no matter what. It's estimated that muscle mass decreases approximately...
Loss Of Movement In Lower Body
Conditions that cause chronic pain can cause severe damage to important components of the joints, thus limiting your ability to move freely. For example, in patients with arthritis, the sustained high levels of inflammation degrade the joint’s cartilage,...
Muscle Weakness And Paralysis
When faced with the alarming symptoms of muscle weakness and paralysis, it's natural to feel a wave of anxiety and frustration. If you are experiencing a loss of control over your own muscles, you may find yourself wondering about the causes of these symptoms...
Causes And Factors Increasing The Risk Of Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction
As you will see, peroneal dysfunction risk factors can range from physical and mechanical disruptions caused by trauma, compression, or bad posture to neurological diseases or other health issues affecting peripheral nerves. Let’s delve into each aspect to better understand the potential triggers for this condition.
Mechanical Factors
Mechanical factors describe your body’s various daily coordinated movements. Holding a certain posture or moving your body in a particular way has the potential risk of contributing to peroneal nerve dysfunction. For example:
- Crossing the legs: Sitting with your legs crossed for long periods can irritate or compress the nerve.
- Tight footwear or leg compression: Wearing ill-fitting shoes, leg splints, or a cast that is too tight may exert pressure on the deep or superficial branches of your perineal nerve.
- Prolonged bed rest: Extended periods of laying in bed can put increased pressure on the nerves and affect normal function.
Traumatic Factors
The peroneal nerve, particularly the common branch, is particularly vulnerable to trauma because it runs close to the skin along the outer side of the knee, where it lacks the protection of robust muscle tissue. Peroneal dysfunction is commonly seen in traumatic events such as:
- Physical injuries: Twisting your knee or putting it in an unnatural position that causes irritation or strain on the nerve might result in nerve damage.
- Fractures: Lower leg bone fractures, generally of the tibia or fibula, have the potential to disrupt the common peroneal nerve and its normal function.
- Direct trauma: One of the most common causes of peroneal nerve dysfunction is a direct blow to the nerve during a traumatic injury such as a sporting incident.
Existing Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions are known to be related to peroneal nerve dysfunction and are often impacted by underlying health issues. These can include:
- Diabetes: The elevated blood sugar levels seen in diabetes can damage peripheral nerves, including the peroneal.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Peroneal nerve dysfunction is a kind of peripheral neuropathy that refers to nerve injury in the outermost parts of the body. This means that peroneal nerve branches can develop peripheral neuropathy.
- Tumor or cyst: When an abnormal growth develops near the peroneal nerve, such as a tumor or infected cyst, the increased pressure may interfere with the nerve’s ability to function properly.
- Autoimmune conditions: Some auto-immune conditions mistakenly attack the body’s nerves, including the peroneal nerve.
Understanding more about these contributing factors and conditions can help you better understand your condition, gain an early diagnosis of peroneal dysfunction, and find a tailored management plan for your symptoms and lifestyle. Let’s look into the topic of diagnosing and treating peroneal dysfunction in the following sections.
Diagnostic Procedure
It’s important to speak to a medical professional so the underlying cause of your discomforts can be diagnosed accurately. A doctor can then prescribe the most appropriate therapy specific to your circumstances.
A variety of tests could be performed to find out if you’re affected by peroneal dysfunction. In the list below, we have set out some of the typical methods you can expect your doctor to use.
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination should be conducted to assess for any sensory limitations, reduction of mobility, signs of inflammation, or other abnormalities that could be contributing to your pain. You can expect the doctor to assess your non-affected leg for comparison purposes.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles and tells a specialist how well the peroneal nerve is transmitting signals to the muscles, identifying if there is dysfunction.
- Magnetic resonance neurography: This imaging technique uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the nerves of the leg. It can provide detailed images of the peroneal nerve, helping identify any serious injuries, abnormalities, or compression.
Completing a comprehensive evaluation of your painful symptoms is important to identify the root cause and ensure you receive a personalized and effective management plan. We hope these insights provide you with an understanding of what to expect when seeking medical help.
Let’s now look into some of the conventional therapies commonly recommended for perineal nerve dysfunction.
Treatment Modalities For Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction
The treatment your doctor recommends will depend on the underlying cause, location, and severity of nerve damage. And if your nerve damage is associated with an underlying health condition, it is important that the issue is addressed.
To help manage the pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility associated with peroneal nerve dysfunction, there is a combination of conservative and surgical treatment options, which we have outlined in the headings below.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative approaches to managing nerve dysfunction should always start with a focus on lifestyle adjustments and less invasive methods. These options aim to alleviate symptoms without resorting to surgery:
- Physical therapy: A tailored program of stretching, balancing, and strengthening exercises can be very beneficial for re-mobilizing and rehabilitating the nerve’s normal functioning movements.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help temporarily address painful symptoms associated with inflammation.
- Steroid injections: An injection of corticosteroid medications acts as a powerful anti-inflammatory and is typically used to reduce high levels of localized swelling and inflammation that impact nerve function.
- Ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) brace: A brace can be helpful for stabilizing the foot or leg to prevent further irritation and damage occurring to the nerve, then allowing it to heal.
Surgical Procedures
In rare cases, surgical intervention may become necessary to address the root cause of dysfunction. Invasive surgical procedures should only be considered if there is a rapid decline of nerve dysfunction that does not respond to conservative treatments or if there are open wounds associated with nerve impairment. Surgeries can include:
- Decompression of the peroneal nerve: The procedure entails treating or removing whatever is impeding the peroneal nerve, such as an abnormal growth or an infected cyst.
- Nerve grafting: Nerve grafting is a more intensive therapy that involves collecting a piece of nerve tissue from another area of your body and using it to restore the damaged pathways of the peroneal nerve.
Understanding these potential treatment options can help you collaborate with your healthcare providers to compose a personalized plan tailored to your specific needs and lifestyle.
We recognize the many complexities of peroneal nerve dysfunction. In the next section, we will discuss how our techniques tackle chronic pain and inflammation to help improve your quality of life.
Managing Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Pain With Neuragenex NFPM
Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management offers a unique approach to alleviate the painful symptoms associated with peroneal nerve dysfunction. Our innovative protocols provide customized treatment programs that aim to relieve nerve pain at a cellular level, providing a path to long-lasting relief.
But most importantly, our comprehensive approach strives to ease pain and inflammation without the need for drugs, chiropractic adjustments, or invasive procedures, instead combining the following methods:
Electroanalgesia
Electroanalgesia is a pain management technique that uses high-pulse electrical current to ease pain, boost blood circulation, improve mobility, and induce...
IV Therapy
IV nutritional therapy, or intravenous therapy, involves administering vital nutrients directly to the bloodstream through an IV. This type of treatment bypasses the digestive system, allowing for maximum absorption and utilization of nutrients by the...
Lifestyle Counseling
Lifestyle counseling is an approach to managing chronic pain that involves identifying, assessing, and modifying lifestyle factors contributing to an individual's pain. For example, lifestyle factors such as nutrition, physical activity, stress, sleep quality...
Read More About Peroneal Nerve Dysfunction Lifestyle Counseling
Proactive Measures To Mitigate The Risk Of Peroneal Nerve Pain
Prevention is a powerful tool to help reduce the risk of peroneal nerve dysfunction from occurring. While there is no one guaranteed way to prevent nerve damage, here are a few great proactive strategies you can adopt into your lifestyle that could make a significant difference:
- Refrain from sitting with your legs crossed.
- Stay physically active.
- Wear protective gear when engaging in high-impact activities.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Manage The Nerve Pain With The Neuragenex NFPM Protocol
We hope the information on this page has helped you better understand the nature of peroneal nerve dysfunction, the various factors and conditions that are usually linked with it, and the importance of exploring the various treatment options available.
While conventional methods can be beneficial for some, for others, it can be challenging to find enduring relief once nerve pain and discomfort have set in. This often has individuals searching for alternative options that provide the long-lasting results they’ve been looking for.
The good news is that the Neuragenex NFPM offers sustainable solutions for those seeking effective, long-lasting relief from the painful symptoms of peroneal nerve dysfunction. Importantly, with our precision of care and protocols that address the root cause of nerve pain, we are proud to offer a path toward a more comfortable and active life without you having to resort to harsh medications or invasive procedures.
The team is here to help you take proactive steps toward easing your pain and improving your mobility. We hope to see you enjoy the activities you love again, free from limitations and discomfort, with a boost to your overall health and well-being.
Put an end to nerve pain. Check how Neuragenex NFPM protocol can help manage pain!