Biphasic Electrical Stimulation
Everything You Need To Know About Biphasic Electrical Stimulation
Read More
May 24, 2023
Electrical stimulation, or e-stim, is a form of therapy that uses electrical signals to trigger muscle contractions, which can provide short-term to long-term pain relief based on the intensity of the e-stim treatment. Medical professionals have used e-stim for decades, and it is now common practice to help treat various issues and conditions, from minor muscle injuries to chronic pain.
However, you should note that there are different e-stim treatment solutions. For example, biphasic e-stim treatment is commonly used by physical therapists to help treat a range of issues.
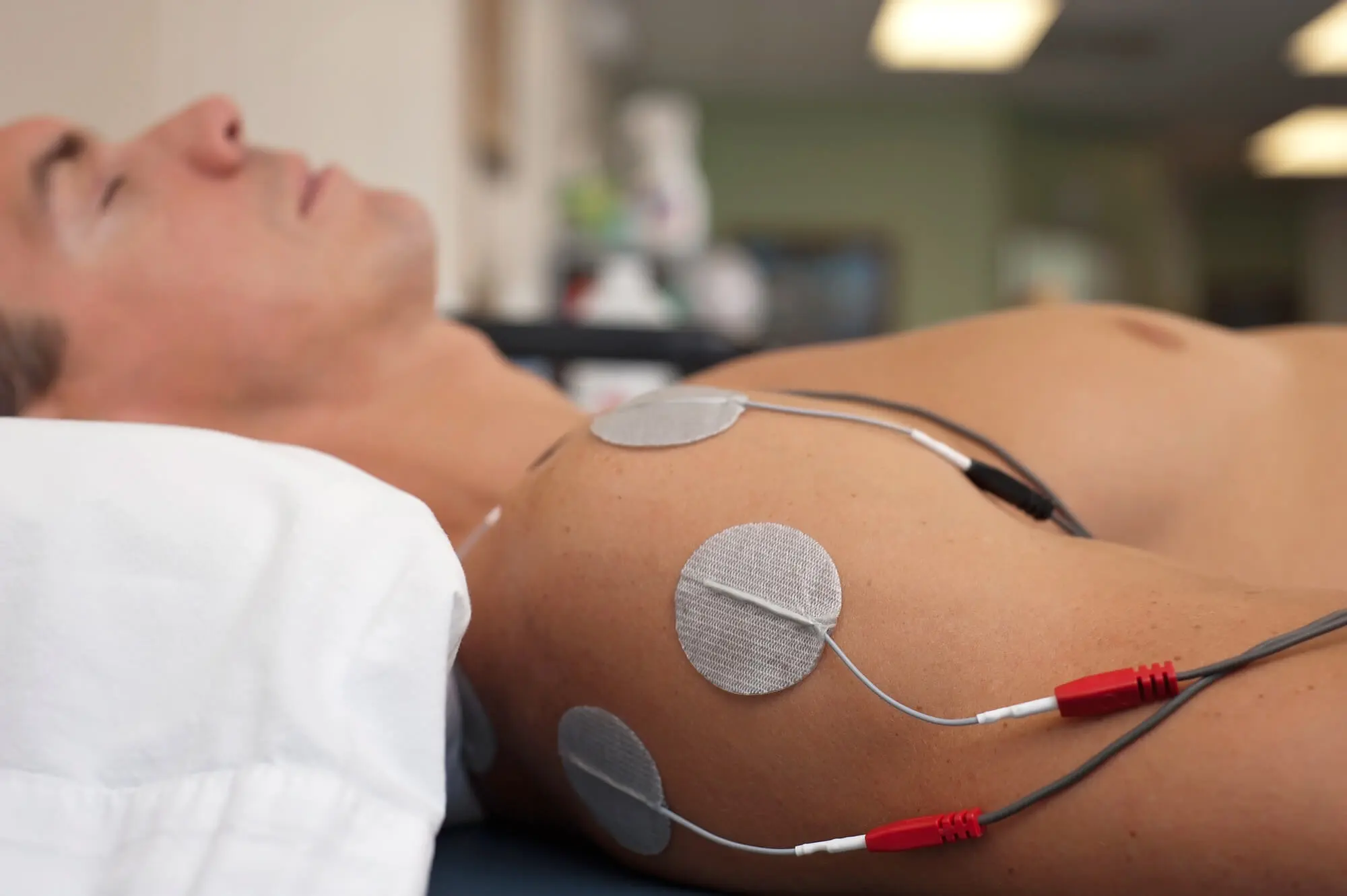
Biphasic electrical stimulation is a type of waveform used in e-stim therapy. It is one of the most commonly used waveforms in e-stim therapy, and it is often used to help strengthen muscles, re-educate muscles, decrease swelling, and increase circulation.
Biphasic electrical stimulation works by sending two different pulses (or phases) at two different intensities that alternate (which is why it’s sometimes known as alternating current therapy as well). This type of e-stim treatment differs from the traditional direct current used in other e-stim solutions, as it does not necessarily use a continuous stream of electricity to stimulate the affected area. Instead, it uses two different pulses, one positive and one negative, that are delivered in quick succession to generate a therapeutic effect.
When it comes to biphasic e-stim treatments, there are two main types. These include symmetrical biphasic waveforms and asymmetrical biphasic waveforms. The following is a breakdown of both types:
Symmetrical biphasic waveforms use identical phases that cancel each other out, thereby producing a zero-net charge. As a result, they are less likely to cause a skin reaction. Symmetrical biphasic waveforms are also less fatiguing than polyphasic waveforms because they require less energy from the device to deliver a therapeutic effect, making them more comfortable for the patient to use.
Symmetrical biphasic waveforms are used by variable muscle stimulator (VMS) units. Because symmetrical biphasic waveforms help generate greater torque with muscle contractions, VMS units are commonly used to help stimulate and strengthen large muscle groups.
Asymmetrical biphasic waveforms consist of non-identical phases that can be either balanced with no net charge or unbalanced, yielding a net charge. Asymmetrical biphasic waveforms are commonly used with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) units, which tend to be more helpful for targeting and strengthening small muscle groups.
Biphasic electrical stimulation works by sending alternating pulses that cause a change in the electrical potential between two points. This produces an electrochemical reaction that causes muscles to contract and relax, depending on the intensity of the electrical stimulus.
The change in electrical potential can help reduce pain and inflammation, in addition to re-educating muscles. This improved muscle response can then be used to help strengthen the affected muscle group and improve overall physical function. It can also improve circulation and reduce swelling.
Because biphasic electrical stimulation can help both small and large muscle groups to contract and relax to reduce inflammation, swelling, and pain, as well as to increase circulation, e-stim units (such as TENS and VMS) are commonly used to treat a variety of conditions and symptoms, including:
Biphasic electrical stimulation can reduce inflammation and improve circulation, which can help reduce acute and chronic pain by relaxing tight muscles, decreasing spasms, and improving blood flow to the area. This increased circulation helps promote healing and reduces pain signals send to the the brain, resulting in a decrease in pain.
Biphasic electrical stimulation can help reduce muscular tension and spasms and improve muscle tone in the affected areas. This improved muscle tone can help reduce back, neck, and shoulder pain caused by muscular or disc syndromes, such as herniated discs, pinched nerves, and sciatica. Additionally, improving muscle strength and range of motion can help reduce the likelihood of future pain and injuries.
Arthritis is inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues that can cause pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. Biphasic electrical stimulation can help improve circulation to the affected area, thereby reducing inflammation and swelling. Additionally, improved muscle contractions and relaxation can help increase the affected joint’s range of motion, reducing stiffness and soreness.
Neuropathies refer to a type of nerve damage that can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the affected area. Biphasic electrical stimulation can relieve these symptoms by helping to reduce inflammation and muscle spasms. Additionally, improved circulation can help the nerve cells to regenerate, reducing pain and restoring sensation in the affected area.
Biphasic electrical stimulation should be avoided in patients with certain cardiac conditions, including those with pacemakers, and any condition that warrants avoiding electrical stimulation, such as open wounds or infections. Additionally, pregnant women and people with epilepsy should not use biphasic electrical stimulation. Finally, patients should always consult with their medical provider before using any type of electrical stimulation to ensure safety and effectiveness.
TENS is a frequently used type of biphasic electrical stimulation, but there is another treatment option available: electroanalgesia. The problem with TENS units is that despite using biphasic waveforms, the pulse rate is low. At most, a TENS unit can only deliver around 400 pulses a second. At-home TENS units have an even lower pulse rate, topping out at 250. Because the pulse rate is so low, the pain neurons being targeted won’t be as affected and can even re-polarize, which means that any relief you might experience from TENS treatment will likely be temporary.
At Relatyv, we use electroanalgesia therapy instead. Electroanalgesia can provide long-term relief because it delivers electrical currents at up to 10,000 pulses per second. A frequency of at least 8300 pulses per second is required to target the neurons’ pain fibers effectively.
E-stim therapy is a safe and effective way to help relieve pain from many conditions. However, it’s essential to understand how e-stim devices work and that not all forms of e-stim are the same. If you’re suffering from chronic pain, you’ll want to choose a type of e-stim therapy that provides long-term relief. As such, consider electroanalgesia as part of our Relatyv protocol to manage chronic pain.
About the Author
Will is a healthcare executive, innovator, entrepreneur, inventor, and writer with a wide range of experience in the medical field. Will has multiple degrees in a wide range of subjects that give depth to his capability as an entrepreneur and capacity to operate as an innovative healthcare executive.
Share on Social Media


You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/
You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/
Neurofunctional Pain Management Overview
Symptoms
Conditions Treated
Treatments
Articles by Category
Locations
Colorado
Wisconsin
Georgia
Hiram
Lawrenceville
Marietta
Powder Springs
Texas
Waco
Victoria
Illinois
Buffalo Grove
New Lenox
St. Charles
Arizona
Tucson
Waddell
Arlington
Avondale
Buckeye
Superior
Mesa
Palo Verde
Morristown
Tempe
Chandler
Anthem
Eloy
Florence
Fort McDowell
Phoenix
El Mirage
Coolidge
Gilbert
Arizona City
Casa Grande
Casa Blanca
Aguila
Sacaton
Apache Junction
Kearny
Stanfield
Goodyear
Litchfield Park
Alabama
Arkansas
California
Florida
Idaho
Indiana
Iowa
Kansas
Louisiana
Maryland
Michigan
Rhode Island
Minnesota
Mississippi
Nevada
New Jersey
New Mexico
North Carolina
Ohio
Pennsylvania
South Dakota
Tennessee
Utah
Virginia
Washington


