It’s estimated that over 20 million Americans suffer from peripheral neuropathy. In fact, many believe it’s significantly higher than that because the condition often goes undiagnosed and untreated. The condition can range from mild to severe and affect a person’s hands, feet, arms, or legs. When severe, peripheral neuropathy can be severely debilitating. Although there’s no cure, per se, there are ways to treat peripheral neuropathy and manage the symptoms effectively to provide long-term pain relief.
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?
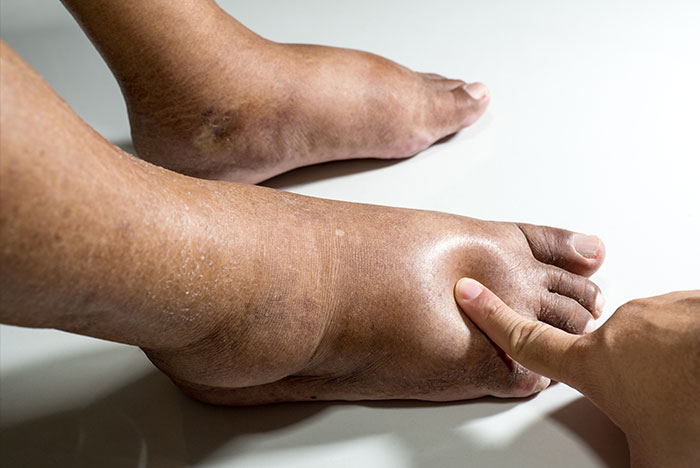
Peripheral neuropathy is a nerve disorder in which the peripheral nerves become damaged or malfunction. This damage or malfunction can be caused by various factors, including disease, injury, metabolic or nutritional problems, toxins, and the side effects of certain medications. The condition often causes numbness, tingling, burning pain, and extreme sensitivity in the affected areas. It can also cause muscle weakness, balance problems, impaired reflexes, and poor coordination.
Where Is The Peripheral Nervous System Located?
The peripheral nervous system is located outside of your brain and spinal cord. It consists of nerves that run throughout your body, connecting it to your brain and spinal cord. These nerves are responsible for sending information back and forth between the different parts of your body. When the peripheral nervous system is damaged, it can cause problems with sensation, movement, and coordination.
Types Of Peripheral Nerves
The peripheral nervous system consists of three main types of peripheral nerves. Any of these nerves can be affected by peripheral neuropathy. With that in mind, the three kinds of peripheral nerves include:
- Autonomic Nerves: These nerves control involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure.
- Sensory Nerves: These nerves carry information from the skin to the brain, such as pain and temperature.
- Motor Nerves: These nerves control movement in the body, such as controlling the muscles in your arms and legs.
Main Types Of Peripheral Neuropathy
There are actually two main types of peripheral neuropathy:
- Demyelinating Neuropathy: This type of peripheral neuropathy occurs when the protective covering of the nerves, called myelin, becomes damaged. This damage can cause the nerve to be unable to transmit signals effectively, resulting in numbness and tingling.
- Axonal Degeneration: This type of peripheral neuropathy occurs when the axon, which is a part of the nerve cell, is damaged due to trauma or disease. This damage can cause the nerve to become less responsive, impairing sensation and movement.
What Happens When You Have Peripheral Neuropathy
When a peripheral nerve becomes damaged, it can cause various symptoms. One common symptom is mild to severe pain, which can be described as burning, stabbing, or aching. Other symptoms include numbness, tingling, weakness, balance problems, impaired reflexes, and a lack of coordination.
In some cases, peripheral neuropathy can end up leading to more severe complications such as muscle wasting, weakened bones, bladder and bowel problems, and even paralysis. Therefore, seeing a doctor for diagnosis and treatment is critical if you experience any of these symptoms.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
A variety of factors can cause peripheral neuropathy. The following are the different causes of peripheral neuropathy:
Diabetes
Diabetes has been linked as one of the main causes of peripheral neuropathy. This is due to the fact that high blood sugar levels may damage the nerves over time by causing a buildup of sugar in the blood, damaging nerve fibers.
Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune diseases like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis can cause nerve damage. The body’s immune system attacks the nerves in these cases because it mistakenly identifies them as a threat.
Infections
Some types of infections, such as HIV, hepatitis C, and Lyme disease, can also damage the nerves. In these cases, the infection attacks the nerve cells directly. As a result, the infection causes inflammation of the nerves, which can result in nerve damage.
Inherited Disorders
Peripheral neuropathy can be the result of an inherited disorder, meaning that a condition leading to peripheral neuropathy is passed down from one generation to the next. Some inherited disorders that can cause peripheral neuropathy include Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and familial amyloid polyneuropathy.
Tumors
Tumors can also cause peripheral neuropathy by compressing or damaging the nerves. Tumors can be benign (which means that they’re non-cancerous) or malignant (meaning they are cancerous). They can affect various nerve types, including motor and sensory nerves.
Bone Marrow Disorders
Bone marrow disorders like myeloma and leukemia can also lead to peripheral neuropathy. These conditions cause an abnormal buildup of white blood cells in the bone marrow. This can compress or damage the nerves over time.
Medications And Toxins
Certain medications and toxins can also cause nerve damage by interfering with how nerves send signals. Examples of medications that can cause peripheral neuropathy include certain chemotherapy drugs, statins, and anti-seizure medications. In addition, exposure to some toxins, such as heavy metals and pesticides, can also damage the nerves.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Your nerves need specific vitamins and minerals to function correctly. Vitamin deficiencies, such as a lack of B vitamins or vitamin E, can lead to nerve damage and peripheral neuropathy. Such damage occurs due to the nerves not receiving enough nutrients, which can cause them to become weak and deteriorate.
Alcoholism
Alcoholism can also cause peripheral neuropathy. Alcohol is toxic to the nerves and, when consumed in large amounts, can make it difficult for the body to absorb certain nutrients, such as B12 vitamins. This can cause the nerves to become nutrient deficient, resulting in damage.
Idiopathic Causes
The cause of peripheral neuropathy can’t always be identified. This is referred to as idiopathic peripheral neuropathy and can still lead to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy differ from one person to another but typically include:
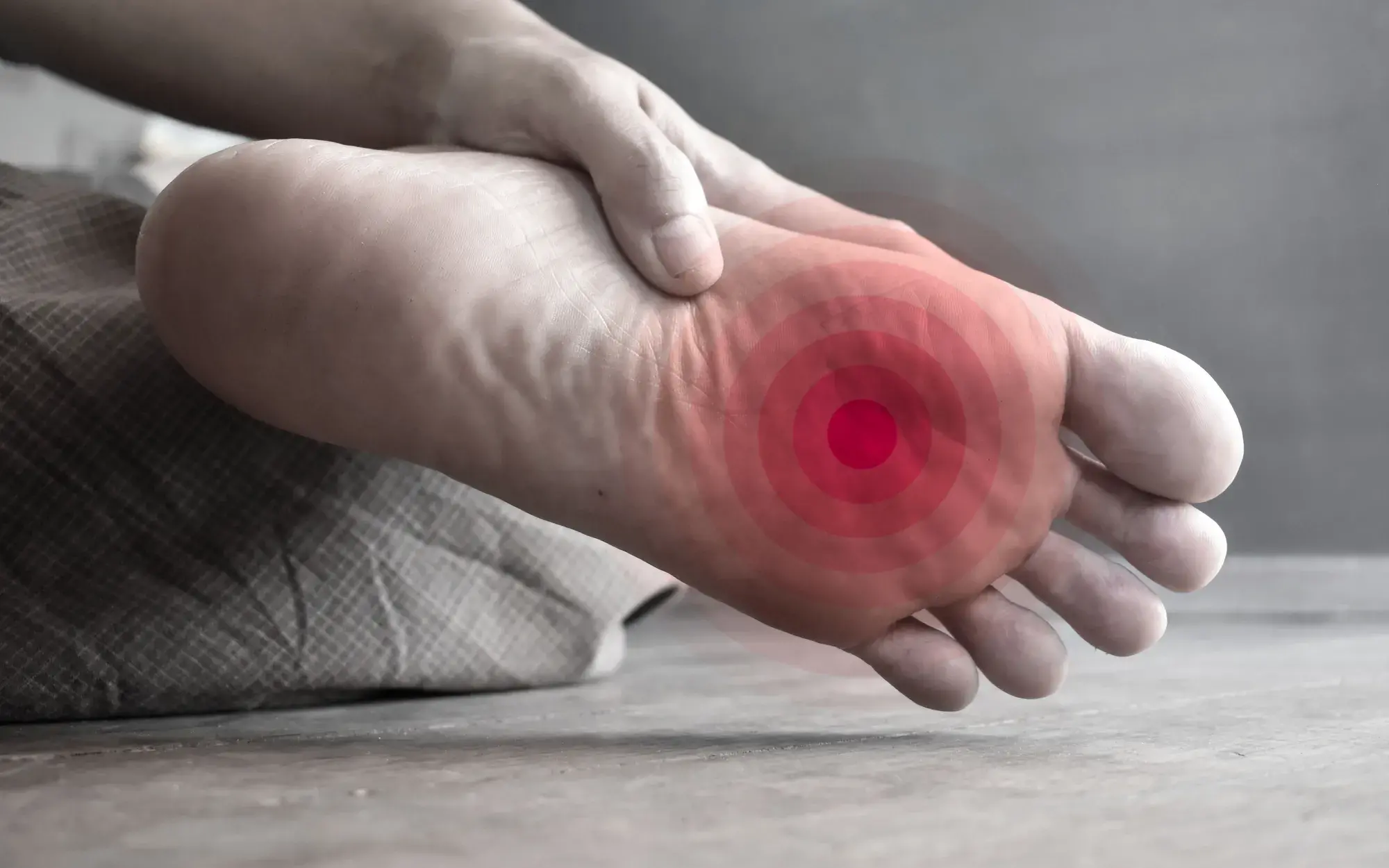
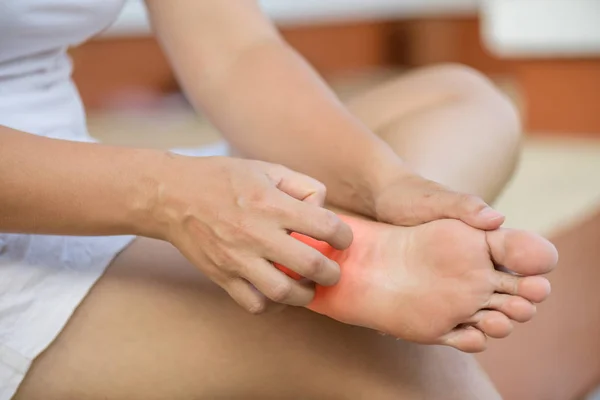
- Nerve Pain: This type of peripheral neuropathy pain is commonly described as burning, tingling, or shooting. This nerve pain may be constant or intermittent and can range from mild to severe.
- Numbness: Patients may experience a sensation of complete numbness in the affected areas.
- Prickling Or Tingling Sensation In The Hands/ Feet: This feeling can be described as a “pins and needles” sensation and typically occurs in the hands and feet. This sensation occurs in areas far away from the brain and spinal cord because the nerve messages being delayed or blocked.
- Lack Of Coordination: Patients with peripheral neuropathy may experience a lack of coordination due to weakened muscles. This can lead to difficulty walking or performing other activities. Additionally, some people may experience balance problems due to poor muscle coordination.
- Muscle Weakness and Paralysis: Muscle weakness can occur if the nerves that control muscle movement are affected by peripheral neuropathy. This can lead to difficulty performing certain activities, such as lifting objects or walking up stairs. In severe cases, muscle paralysis may occur, meaning the affected muscles cannot move.
Muscle Weakness And Paralysis
When faced with the alarming symptoms of muscle weakness and paralysis, it's natural to feel a wave of anxiety and frustration. If you are experiencing a loss of control over your own muscles, you may find yourself wondering about the causes of these symptoms...
Muscle Spasm In The Arm
Experiencing muscle spasms in the arm can be quite uncomfortable and disruptive, as they may interrupt your daily life. However, with the right understanding and treatment approaches, they don’t have to stop you from doing the activities you enjoy. Whether...
Muscle Spasm
Muscle spasms are sudden, involuntary contractions of one or more muscles. These contractions can be painful and cause your muscles to tighten up or go into a knot. Muscle spasms can affect any muscle in the body and may last from a few seconds to several...
Hand Weakness
Experiencing persistent weakness in your hands can significantly impact your quality of life. If you have weakness in your hands, it can be difficult to perform everyday tasks. It can be especially problematic if you use your hands to perform your job. If you...
Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment describes any decline in cognitive abilities, such as memory, language, problem-solving, and attention. Such impairments can be a sign of more serious conditions, such as dementia or Alzheimer's disease, but they can also be the result of...
Muscle Spasm In Back Of Thigh
Besides causing ongoing discomfort, chronic pain can significantly decrease your quality of life, increase the risk of other mental and physical disorders, and cause you to deal with astronomical healthcare costs....
Pins And Needles
Everyone experiences paresthesia at least once in their lives. Think, for example, of when you’ve been sitting cross-legged for too long and you have the sensation that your limb has “fallen asleep.” Or it can happen while you are asleep, often because...
Neuralgia
The nerves across our bodies enable muscle movement, control essential functions, and process touch and temperature sensations. Ultimately, they play a vital role in helping us experience the world around...
Numbness And Tingling In Fingers
Experiencing numbness and tingling in the fingers can be quite unsettling. It can feel like a strange sensation that starts with a subtle loss of feeling, followed by a tingling or “pins and needles” effect that can range from mild to intense. Over time,...
Sensation Of Numbness
Feeling a numbness in your body can be a scary and uncomfortable experience. This numbness, also known as paresthesia, is a tingling or prickling sensation that can occur anywhere in the body. It is often described as feeling like pins and needles or a loss...
Stomach Is Swollen and Bloated
Abdominal bloating and swelling, also known as 'abdominal distention,' are two very common yet complex gastrointestinal complaints. Although these terms...
Lower Leg Muscle Loss
Muscle atrophy is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Although there are many different reasons why muscles begin to atrophy, it also tends to happen naturally, no matter what. It's estimated that muscle mass decreases approximately...
Risk Factors
Because there are so many types of conditions and causes that can lead to peripheral neuropathy, there are also various risk factors. These include:
- High Blood Sugar Levels: One of the reasons why people who have diabetes are at an increased risk for developing peripheral neuropathy is because high blood sugar levels can potentially damage the nerves over time.
- Alcohol Abuse: Long-term alcohol abuse can damage your nerves because alcohol can interfere with the nerves’ ability to send signals.
- Unhealthy Diets: Poor nutrition can lead to a lack of essential vitamins and minerals, which can cause damage to your nerves.
- Autoimmune Disease: Certain autoimmune diseases can cause an abnormal immune response that affects the nerves.
- Kidney, Liver, or Thyroid Disorders: These illnesses can interfere with the proper functioning of nerves because they affect the body’s ability to absorb or use certain nutrients needed to maintain healthy nerves.
- Toxin Exposure: Environmental toxins and heavy metals, such as lead or arsenic, can lead to nerve damage over time.
- Repetitive Motions: The peripheral nerves can be damaged by repetitive motions or strain, such as typing for long periods without taking breaks or playing an instrument without proper hand and wrist positioning.
- Genetics and Family History: Some people may be more likely to develop peripheral neuropathy if they have a family history of the condition.
Complications
Because peripheral neuropathy can affect the muscles’ ability to move and sense feeling, some potential complications can arise. These include:
- Falls: Nerve damage can cause weak muscles, poor balance, and a lack of coordination, increasing the risk of falls.
- Burns and Skin Injuries: Damage to the nerves can reduce sensation in the affected areas, leading to an increased risk for burns and skin injuries.
- Infections: Reduced sensation in the feet can make recognizing signs of infection difficult, such as redness and swelling.
Diagnosis For Peripheral Neuropathy
Before you begin treatment, your doctor will do a physical exam to look for potential signs of nerve damage. They will also likely order blood tests and imaging scans (such as MRIs and CT scans) to rule out different possible underlying causes causing the symptoms. Other diagnostic tests a doctor may order include:
- Electromyography (EMG): An EMG test measures the electrical activity in your muscles to help diagnose nerve damage.
- Nerve Conduction Study: This test measures how quickly electrical signals travel through the nerves.
- Quantitative Sensory Testing (QST): This type of skin test evaluates temperature and vibration sensation in different parts of your body.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a doctor may perform a nerve biopsy to look for tissue abnormalities that may indicate nerve damage.
What Can Be Mistaken For Peripheral Neuropathy
An accurate diagnosis is critical to ensuring your condition is effectively treated. Unfortunately, peripheral neuropathy causes similar symptoms to a variety of other conditions. The following are the potential conditions that can be mistaken for peripheral neuropathy if improperly diagnosed:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS is an autoimmune disorder affecting the central nervous system and causes many symptoms, including numbness in the extremities, difficulty walking, and vision problems.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Carpal tunnel syndrome tends to develop when the median nerve in the wrist is compressed, leading to numbness, pain, and tingling in the hand.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia can lead to widespread muscle pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances.
- Pinched Nerves: Pinched nerves occur when a nerve is compressed or irritated, leading to symptoms similar to peripheral neuropathy.
- Arthritis: Arthritis can lead to inflammation in the joints, thereby causing pain, stiffness, and numbness.
Treatment Options
Treatment for peripheral neuropathy typically focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the condition and relieving any associated symptoms. Depending on your diagnosis, treatment may involve various home remedies, prescriptions, non-invasive treatments, and surgical procedures. These include the following:
Home Remedies For Pain Relief
Home remedies are typically recommended for milder symptoms and are usually only effective at providing short-term relief. They can include the following:
- Heat and Cold Packs: Applying heat or cold packs to the area affected by peripheral neuropathy can help relieve pain and inflammation. This is because heat or cold can reduce nerve sensitivity and encourage blood flow.
- Rest: Taking regular breaks and getting plenty of rest can help reduce the severity of symptoms by allowing the body to recover.
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and relieve short-term pain. Ibuprofen is an example of a common NSAID.
- Ointments and Creams: Ointments and creams containing capsaicin, menthol, lidocaine, or other ingredients can help reduce pain when rubbed into the skin by numbing nerve endings and reducing inflammation.
Prescription Treatments
Doctors may prescribe pain medications and other types of treatment solutions depending on the cause and severity of the condition. These include:
- Pain Medication: Pain medication, such as opioids, may be prescribed to help manage severe pain. Common opioids used for pain relief include oxycodone, hydrocodone, and codeine. It’s important to understand that such medications can be effective at providing short-term relief, but they can also be habit-forming, making them a risky treatment option.
- Medication For Epilepsy: Anti-seizure medications such as gabapentin and pregabalin can reduce nerve pain by blocking signals between the brain and nerves.
- Duloxetine: Duloxetine is a medication that is often used to treat depression and anxiety. It can also help reduce nerve pain by targeting neurochemicals in the brain involved in pain perception.
- Antidepressants: Doctors may also prescribe certain antidepressants to help manage nerve pain. Antidepressants typically work by blocking the reabsorption of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate pain perception.
- Skin Patches: Skin patches containing a topical anesthetic (such as lidocaine) are applied to the skin to provide localized pain relief.
- Podiatric Treatments: Podiatric treatments such as orthotics, braces, and padding can help reduce pressure on the feet.
- Braces and Canes: Braces and canes can help reduce joint strain and support weakened muscles.
Non-Pharmaceutical Treatment Options
There are also non-pharmaceutical treatments available for peripheral neuropathy. These treatments are often less risky than traditional methods and can offer long-term relief. Examples include:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can help reduce muscle tension and inflammation, as well as improve strength, flexibility, and joint mobility. Physical therapy helps reduce pain, strengthen weakened muscles, improve the flexibility of your extremities, and improve your balance and control of movement.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese treatment that is used to stimulate pressure points in the body using thin needles. Doing so can help keep the nerves active and engaged by stimulating blood flow. It’s worth noting that although some patients have found success with acupuncture, more research is needed to determine its efficacy.
Surgical Treatment Options
In severe cases of peripheral neuropathy, doctors may recommend surgery. However, surgery is incredibly invasive, and, as such, there are a lot of potential risks. These risks can include infection, excessive bleeding, and nerve damage. Not to mention, surgery can be expensive, result in long recovery times, and may not even successfully alleviate the symptoms.
Therefore, it’s essential to discuss the risks and benefits of any type of invasive treatment with your doctor before making a decision. Potential surgical procedures include:
- Reconnecting Nerves: If the nerves have been damaged, surgery may be necessary to reconnect them. This is done by separating the healthy nerves from the damaged ones and then reattaching them.
- Reducing Nerve Compression: Nerve compression can be relieved with surgery by cutting out parts of the bone or soft tissue that puts pressure on the nerve.
How To Live With Peripheral Neuropathy
Living with peripheral neuropathy can be challenging due to the nature of the symptoms. Not only can the symptoms themselves be distressing, but they can also lead to other health issues that might have otherwise been avoided. As such, peripheral neuropathy can impact your quality of life in the following ways:
- You may not realize you’ve experienced an injury or wound if you suffer from numbness due to peripheral neuropathy. If you cannot sense these issues, they can worsen due to a lack of treatment. In severe cases, these problems can lead to gangrene and the need for amputations.
- Damage to your autonomic nerves can make regulating your body temperature or sweating challenging, which can be dangerous in certain situations. It can also lead to cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, resulting in an irregular heartbeat that may increase your risk of heart attack.
- Autonomic nerve damage can also cause digestive issues, such as constipation and bloating. Additionally, these digestive problems can worsen due to the side effects of various medications used to treat peripheral neuropathy.
- The autonomic and motor nerves are crucial to the function of the urinary system. As such, damage to these nerves could lead to bladder control problems.
How Peripheral Neuropathy Affects Loved Ones
Peripheral neuropathy can take an emotional and physical toll on the sufferer and their loved ones. The physical severity of peripheral neuropathy symptoms can be taxing on the person’s overall health and well-being, leading to long-term physical limitations. This can be difficult for a loved one to witness, especially if the sufferer cannot do activities they once enjoyed.
The emotional strain of managing a chronic condition can also be overwhelming for the person with peripheral neuropathy and their loved ones. The sufferer may struggle to come to terms with their condition and the limitations it places on them. At the same time, those close to them may feel helpless when it comes to providing support.
Additionally, many people’s lack of understanding about peripheral neuropathy may cause feelings of isolation and frustration in the sufferer, which can be difficult for their loved ones to witness and manage. However, those close to the sufferer need to remember that peripheral neuropathy is a real medical condition, and the sufferer should not be judged or feel embarrassed by their symptoms.
A better understanding of peripheral neuropathy can help loved ones better support the sufferer. Researching and discussing the condition with healthcare professionals is a great place to start. Additionally, providing emotional support and a listening ear can help sufferers feel understood and loved despite their medical condition.
Is Peripheral Neuropathy Treatable?
When treating peripheral neuropathy, you’ll find that there are lots of ways to address the symptoms. However, there is no single treatment solution that is a cure-all. Additionally, your condition’s underlying causes must be treated. This is the only way to address peripheral neuropathy and potentially find long-term relief. Unfortunately, many conventional treatment solutions traditional doctors recommend are merely short-term solutions to offer temporary pain relief.
Fortunately, there are other options than these solutions. You can treat peripheral neuropathy in a way that is safe and effective for your long-term health and well-being. For example, this can be done using a Neurofunctional Pain Management approach.
Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management For Peripheral Neuropathy
We believe that Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management is the best way to treat peripheral neuropathy. This approach involves addressing the underlying causes of pain and other symptoms that are associated with peripheral neuropathy. This includes identifying and treating the underlying root causes of nerve damage, such as diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, or other medical conditions.
Additionally,Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management focuses on improving the functioning of nerves and reestablishing normal nerve signals to reduce pain. We use several treatment solutions, including electroanalgesia therapy, IV therapy, and lifestyle counseling, as part of the protocol. This whole-person approach to treating peripheral neuropathy is designed to help restore balance in the nervous system and reduce pain and other symptoms, while also providing long-term relief.
Electroanalgesia
Electroanalgesia is a pain management technique that uses high-pulse electrical current to ease pain, boost blood circulation, improve mobility, and induce...
IV Therapy
IV nutritional therapy, or intravenous therapy, involves administering vital nutrients directly to the bloodstream through an IV. This type of treatment bypasses the digestive system, allowing for maximum absorption and utilization of nutrients by the...
Lifestyle Counseling
Lifestyle counseling is an approach to managing chronic pain that involves identifying, assessing, and modifying lifestyle factors contributing to an individual's pain. For example, lifestyle factors such as nutrition, physical activity, stress, sleep quality...
Get Relief From Peripheral Neuropathy
Neuragenex Neurofunctional Pain Management strive to be the first thought, first choice, and the first step for those seeking relief from peripheral neuropathy. Our goal is to give our patients compassionate, personalized care and cutting-edge treatments to help them experience lasting relief from their symptoms. We focus on treating the whole person by combining traditional methods with innovative therapies to ensure our patients get the best possible care. We are committed to helping those with peripheral neuropathy find relief and reclaim their quality of life.
Trying out different options to no avail can be exhausting.